A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Indiana | |
|---|---|
| State of Indiana | |
| Nickname: "The Hoosier State" | |
| Motto: | |
| Anthem: "On the Banks of the Wabash, Far Away" [1] | |
 Map of the United States with Indiana highlighted | |
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Indiana Territory |
| Admitted to the Union | December 11, 1816 (19th) |
| Capital (and largest city) | Indianapolis |
| Largest county or equivalent | Marion |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Indianapolis |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Eric Holcomb (R) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Suzanne Crouch (R) |
| Legislature | General Assembly |
| • Upper house | Indiana Senate |
| • Lower house | Indiana House of Representatives |
| Judiciary | Indiana Supreme Court |
| U.S. senators |
|
| U.S. House delegation |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 36,418 sq mi (94,321 km2) |
| • Land | 35,868 sq mi (92,897 km2) |
| • Water | 550 sq mi (1,424 km2) 1.5% |
| • Rank | 38th |
| Dimensions | |
| • Length | 270 mi (435 km) |
| • Width | 140 mi (225 km) |
| Elevation | 700 ft (210 m) |
| Highest elevation | 1,257 ft (383 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 320 ft (97 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 6,785,528[3] |
| • Rank | 17th |
| • Density | 189/sq mi (73.1/km2) |
| • Rank | 16th |
| • Median household income | $62,743 (2,021)[4] |
| • Income rank | 37th |
| Demonym | Hoosier |
| Language | |
| • Official language | English |
| Time zones | |
| 80 counties | UTC−05:00 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−04:00 (EDT) |
| 12 counties | UTC−06:00 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−05:00 (CDT) |
| USPS abbreviation | IN |
| ISO 3166 code | US-IN |
| Traditional abbreviation | Ind. |
| Latitude | 37° 46′ N to 41° 46′ N |
| Longitude | 84° 47′ W to 88° 6′ W |
| Website | in |
| List of state symbols | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Poem | "Indiana"[5] |
| Slogan | "IN Indiana"[6] |
| Living insignia | |
| Bird | Northern cardinal[7] (Cardinalis cardinalis) |
| Flower | Peony[8] (Paeonia) |
| Insect | Say's firefly[9] (Pyractomena angulata) |
| Tree | Tulip tree[8] (Liriodendron tulipifera) |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Color(s) | Blue and gold |
| Firearm | Grouseland Rifle[10] |
| Food | Popcorn (state snack)[11] |
| Fossil | Mastodon[12] (Mammut americanum) |
| Rock | Indiana limestone[13] |
| Other | Wabash River (state river)[13] Republic P-47 Thunderbolt Hoosier Spirit II (state aircraft)[14] |
| State route marker | |
 | |
| State quarter | |
 Released in 2002 | |
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Indiana (/ˌɪndiˈænə/ IN-dee-AN-ə)[15] is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the south and southeast, and the Wabash River and Illinois to the west. Nicknamed "the Hoosier State",[16] Indiana is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th state on December 11, 1816.
Various indigenous peoples inhabited what would become Indiana for thousands of years, some of whom the U.S. government expelled between 1800 and 1836. Indiana received its name because the state was largely possessed by native tribes even after it was granted statehood. Since then, settlement patterns in Indiana have reflected regional cultural segmentation present in the Eastern United States; the state's northernmost tier was settled primarily by people from New England and New York, Central Indiana by migrants from the Mid-Atlantic states and adjacent Ohio, and Southern Indiana by settlers from the Upland South, particularly Kentucky and Tennessee.[17]
Indiana has a diverse economy with a gross state product of $352.62 billion in 2021.[18] It has several metropolitan areas with populations greater than 100,000 and a number of smaller cities and towns. Indiana is home to professional sports teams, including the NFL's Indianapolis Colts and the NBA's Indiana Pacers. The state also hosts several notable competitive events, such as the Indianapolis 500, held at Indianapolis Motor Speedway.
Etymology
Indiana's name means "Land of the Indians", or simply "Indian Land".[b] It also stems from Indiana's territorial history. On May 7, 1800, the United States Congress passed legislation to divide the Northwest Territory into two areas and named the western section the Indiana Territory. In 1816, when Congress passed an Enabling Act to begin the process of establishing statehood for Indiana, a part of this territorial land became the geographic area for the new state.[c][19][20]
Formal use of the word Indiana dates from 1768, when a Philadelphia-based trading company gave its land claim in present-day West Virginia the name "Indiana" in honor of its previous owners, the Iroquois. Later, ownership of the claim was transferred to the Indiana Land Company, the first recorded use of the word Indiana. But the Virginia colony argued that it was the rightful owner of the land because it fell within its geographic boundaries. The U.S. Supreme Court denied the land company's right to the claim in 1798.[21]
Hoosier
A native or resident of Indiana is known as a Hoosier.[22] The etymology of this word is disputed, but the leading theory, advanced by the Indiana Historical Bureau and the Indiana Historical Society, has its origin in Virginia, Kentucky, the Carolinas, and Tennessee (the Upland South) as a term for a backwoodsman, a rough countryman, or a country bumpkin.[23][24]
History
Indigenous inhabitants

The first inhabitants in what is now Indiana were the Paleo-Indians, who arrived about 8000 BC after the melting of the glaciers at the end of the Ice Age. Divided into small groups, the Paleo-Indians were nomads who hunted large game such as mastodons. They created stone tools made out of chert by chipping, knapping and flaking.[25]
The Archaic period, which began between 5000 and 4000 BC, covered the next phase of indigenous culture. The people developed new tools as well as techniques to cook food, an important step in civilization. These new tools included different types of spear points and knives, with various forms of notches. They made ground-stone tools such as stone axes, woodworking tools and grinding stones. During the latter part of the period, they built earthwork mounds and middens, which showed settlements were becoming more permanent. The Archaic period ended at about 1500 BC, although some Archaic people lived until 700 BC.[25]
The Woodland period began around 1500 BC when new cultural attributes appeared. The people created ceramics and pottery and extended their cultivation of plants. An early Woodland period group named the Adena people had elegant burial rituals, featuring log tombs beneath earth mounds. In the middle of the Woodland period, the Hopewell people began to develop long-range trade of goods. Nearing the end of the stage, the people developed highly productive cultivation and adaptation of agriculture, growing such crops as corn and squash. The Woodland period ended around 1000 AD.[25]
The Mississippian culture emerged, lasting from 1000 AD until the 15th century, shortly before the arrival of Europeans. During this stage, the people created large urban settlements designed according to their cosmology, with large mounds and plazas defining ceremonial and public spaces. The concentrated settlements depended on the agricultural surpluses. One such complex was the Angel Mounds. They had large public areas such as plazas and platform mounds, where leaders lived or conducted rituals. Mississippian civilization collapsed in Indiana during the mid-15th century for reasons that remain unclear.[25]
The historic Native American tribes in the area at the time of European encounter spoke different languages of the Algonquian family. They included the Shawnee, Miami, and Illini. Refugee tribes from eastern regions, including the Delaware who settled in the White and Whitewater River Valleys, later joined them.
European exploration and sovereignty

In 1679, French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle was the first European to cross into Indiana after reaching present-day South Bend at the St. Joseph River.[26] He returned the following year to learn about the region. French-Canadian fur traders soon arrived, bringing blankets, jewelry, tools, whiskey and weapons to trade for skins with the Native Americans.
By 1702, Sieur Juchereau established the first trading post near Vincennes. In 1715, Sieur de Vincennes built Fort Miami at Kekionga, now Fort Wayne. In 1717, another Canadian, Picote de Beletre, built Fort Ouiatenon on the Wabash River, to try to control Native American trade routes from Lake Erie to the Mississippi River.
In 1732, Sieur de Vincennes built a second fur trading post at Vincennes. French Canadian settlers, who had left the earlier post because of hostilities, returned in larger numbers. In a period of a few years, British colonists arrived from the East and contended against the Canadians for control of the lucrative fur trade. Fighting between the French and British colonists occurred throughout the 1750s as a result.
The Native American tribes of Indiana sided with the French Canadians during the French and Indian War (also known as the Seven Years' War). With British victory in 1763, the French were forced to cede to the British crown all their lands in North America east of the Mississippi River and north and west of the colonies.
The tribes in Indiana did not give up: they captured Fort Ouiatenon and Fort Miami during Pontiac's Rebellion. The British royal proclamation of 1763 designated the land west of the Appalachians for Native American use, and excluded British colonists from the area, which the Crown called "Indian Territory".
In 1775, the American Revolutionary War began as the colonists sought self-government and independence from the British. The majority of the fighting took place near the East Coast, but the Patriot military officer George Rogers Clark called for an army to help fight the British in the west.[27] Clark's army won significant battles and took over Vincennes and Fort Sackville on February 25, 1779.[28]
During the war, Clark managed to cut off British troops, who were attacking the eastern colonists from the west. His success is often credited for changing the course of the American Revolutionary War.[29] At the end of the war, through the Treaty of Paris, the British crown ceded their claims to the land south of the Great Lakes to the newly formed United States, including Native American lands.
The frontier
In 1787, the U.S. defined the Northwest Territory which included the area of present-day Indiana. In 1800, Congress separated Ohio from the Northwest Territory, designating the rest of the land as the Indiana Territory.[30] President Thomas Jefferson chose William Henry Harrison as the governor of the territory, and Vincennes was established as the capital.[31] After the Michigan Territory was separated and the Illinois Territory was formed, Indiana was reduced to its current size and geography.[30]
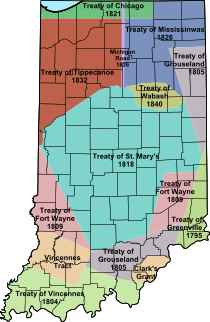
Starting with the Battle of Fallen Timbers in 1794 and the Treaty of Greenville in 1795, Native American titles to Indiana lands were extinguished by usurpation, purchase, or war and treaty. About half the state was acquired in the Treaty of St. Mary's from the Miami in 1818. Purchases were not complete until the Treaty of Mississinewas in 1826 acquired the last of the reserved Native American lands in the northeast.
A portrait of the Indiana frontier about 1810: The frontier was defined by the Treaty of Fort Wayne in 1809, adding much of the southwestern lands around Vincennes and southeastern lands adjacent to Cincinnati, to areas along the Ohio River as part of U.S. territory. Settlements were military outposts such as Fort Ouiatenon in the northwest and Fort Miami (later Fort Wayne) in the northeast, Fort Knox and Vincennes settlement on the lower Wabash. Other settlements included Clarksville (across from Louisville), Vevay, and Corydon along the Ohio River, the Quaker Colony in Richmond on the eastern border, and Conner's Post (later Connersville) on the east central frontier. Indianapolis would not be populated for 15 more years, and central and northern Indiana Territory remained wilderness populated primarily by Indigenous communities. Only two counties in the extreme southeast, Clark and Dearborn, had been organized by European settlers. Land titles issued out of Cincinnati were sparse. Settler migration was chiefly via flatboat on the Ohio River westerly, and by wagon trails up the Wabash/White River Valleys (west) and Whitewater River Valleys (east).
In 1810, the Shawnee tribal chief Tecumseh and his brother Tenskwatawa encouraged other indigenous tribes in the territory to resist European settlement. Tensions rose and the U.S. authorized Harrison to launch a preemptive expedition against Tecumseh's Confederacy; the U.S. gained victory at the Battle of Tippecanoe on November 7, 1811. Tecumseh was killed in 1813 during the Battle of Thames. After his death, armed resistance to United States control ended in the region. Most Native American tribes in the state were later removed to west of the Mississippi River in the 1820s and 1830s after U.S. negotiations and the purchase of their lands.[32]
Statehood and settlement
Corydon, a town in the far southern part of Indiana, was named the second capital of the Indiana Territory in May 1813 in order to decrease the threat of Native American raids following the Battle of Tippecanoe.[30] Two years later, a petition for statehood was approved by the territorial general assembly and sent to Congress. An Enabling Act was passed to provide an election of delegates to write a constitution for Indiana. On June 10, 1816, delegates assembled at Corydon to write the constitution, which was completed in 19 days. Jonathan Jennings was elected the fledgling state's first governor in August 1816. President James Madison approved Indiana's admission into the union as the nineteenth state on December 11, 1816.[28] In 1825, the state capital was moved from Corydon to Indianapolis.[30]
 |
 |
Many European immigrants went west to settle in Indiana in the early 19th century. The largest immigrant group to settle in Indiana were Germans, as well as many immigrants from Ireland and England. Americans who were primarily ethnically English migrated from the Northern Tier of New York and New England, as well as from the mid-Atlantic state of Pennsylvania.[34][35] The arrival of steamboats on the Ohio River in 1811, and the National Road at Richmond in 1829, greatly facilitated settlement of northern and western Indiana.
Following statehood, the new government worked to transform Indiana from a frontier into a developed, well-populated, and thriving state, beginning significant demographic and economic changes. In 1836, the state's founders initiated a program, the Indiana Mammoth Internal Improvement Act, that led to the construction of roads, canals, railroads and state-funded public schools. The plans bankrupted the state and were a financial disaster, but increased land and produce value more than fourfold.[36] In response to the crisis and in order to avert another, in 1851, a second constitution was adopted. Among its provisions were a prohibition on public debt, as well as the extension of suffrage to African-Americans.
Civil War and late 19th century industry
During the American Civil War, Indiana became politically influential and played an important role in the affairs of the nation. Indiana was the first western state to mobilize for the United States in the war, and soldiers from Indiana participated in all the war's major engagements. The state provided 126 infantry regiments, 26 batteries of artillery and 13 regiments of cavalry to the Union.[37]
In 1861, Indiana was assigned a quota of 7,500 soldiers to join the Union Army.[38] So many volunteered in the first call that thousands had to be turned away. Before the war ended, Indiana had contributed 208,367 men. Casualties were over 35% among these men: 24,416 lost their lives and over 50,000 more were wounded.[39] The only Civil War conflicts fought in Indiana were the Newburgh Raid, a bloodless capture of the city; and the Battle of Corydon, which occurred during Morgan's Raid leaving 15 dead, 40 wounded, and 355 captured.[40]
After the war, Indiana remained a largely agricultural state. Post-war industries included mining, including limestone extraction; meatpacking; food processing, such as milling grain, distilling it into alcohol; and the building of wagons, buggies, farm machinery, and hardware.[41] However, the discovery of natural gas in the 1880s in northern Indiana led to an economic boom: the abundant and cheap fuel attracted heavy industry; the availability of jobs, in turn, attracted new settlers from other parts of the country as well as from Europe.[42] This led to the rapid expansion of cities such as South Bend, Indianapolis, and Fort Wayne.[41]
Early 20th century
The early decades of the 20th century saw Indiana develop into a leading manufacturing state with heavy industry concentrating in the north.[34] In 1906 the United States Steel Corporation created a new industrial city on Lake Michigan, Gary, named after Elbert Henry Gary, its founding chairman. With industrialization, workers developed labor unions (their strike activities induced governor James P. Goodrich to declare martial law in Gary in 1919)[43] and a socialist party.[44] Railroader Eugene Debs of Terre Haute, the Socialist candidate received 901,551 votes (6.0% of the national vote) in the 1912 presidential election.[45] Suffrage movements also arose to enfranchise women.[42]
In its earlier years, Indiana was a leader in the automobile boom. Beginning its production in Kokomo in 1896, Haynes-Apperson was the nation's first commercially successful auto company.[46] The importance of vehicle and parts manufacture to the state was symbolized by the construction in 1909 of the Indianapolis Motor Speedway.[47]
In the 1920s, state politics was heavily influenced by the rise of the Indiana Klan. First organized in 1915 as a branch of the Ku Klux Klan, it appealed to white Protestants alarmed by social and economic trends, including changes induced by immigration from southern and central Europe.[48] In the name of defending "hundred-per-cent Americanism", the Klan sought exclude from public life "Bolsheviks, Catholics, Jews, Negroes, bootleggers, pacifists, evolutionists, foreigners, and all persons it considered immoral".[49]
By 1925 the Klan had 250,000 members, an estimated 30% of native-born white men.[50][51] By 1925 over half the elected members of the Indiana General Assembly, the governor of Indiana, and many other high-ranking officials in local and state government were members of the Klan. Politicians had also learned they needed Klan endorsement to win office.[52] That year, "Grand Dragon" D.C. Stephenson, who had begun to brag "I am the law in Indiana",[53] was charged and convicted for the rape and murder of Madge Oberholtzer, a young schoolteacher. Denied pardon, in 1927 Stephenson gave the Indianapolis Times lists of people the Klan had paid. Partly as a result of compounded scandal, membership collapsed.[54]
Throughout the 1930s, Democrats were in power and "the Klan was political poison".[55] During those years, Indiana, like the rest of the nation, was affected by the Great Depression. The economic downturn had a wide-ranging negative impact on Indiana, such as the decline of urbanization. The Dust Bowl to the west led many migrants to flee to the more industrialized Midwest. Governor Paul V. McNutt's administration struggled to build a state-funded welfare system to help overwhelmed private charities. During his administration, spending and taxes were both cut drastically in response to the Depression, and the state government was completely reorganized. McNutt ended Prohibition in the state and enacted the state's first income tax. On several occasions, he declared martial law to put an end to worker strikes.[56]
World War II helped lift Indiana's economy, as the war required steel, food and other goods the state produced.[57] Roughly 10% of Indiana's population joined the armed forces, while hundreds of industries earned war production contracts and began making war material.[58] Indiana manufactured 4.5% of total U.S. military armaments during World War II, ranking eighth among the 48 states.[59] The expansion of industry to meet war demands helped end the Great Depression.[57]
Modern era
With the conclusion of World War II, Indiana rebounded to pre-Depression levels of production. Industry became the primary employer, a trend that continued into the 1960s. Urbanization during the 1950s and 1960s led to substantial growth in the state's cities. The auto, steel and pharmaceutical industries topped Indiana's major businesses. Indiana's population continued to grow after the war, exceeding five million by the 1970 census.[60] In the 1960s the administration of Matthew E. Welsh adopted its first sales tax of 2%.[61] Indiana schools were desegregated in 1949. In 1950, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Indiana's population as 95.5% white and 4.4% black.[62] Governor Welsh also worked with the General Assembly to pass the Indiana Civil Rights Bill, granting equal protection to minorities in seeking employment.[63]
On December 8, 1964, a Convair B-58 carrying nuclear weapons slid off an icy runway on Bunker Hill Air Force Base in Bunker Hill, Indiana and caught fire during a training drill. The five nuclear weapons on board were burned, including one 9-megaton thermonuclear weapon, causing radioactive contamination of the crash area.[64]
Beginning in 1970, a series of amendments to the state constitution were proposed. With adoption, the Indiana Court of Appeals was created and the procedure of appointing justices on the courts was adjusted.[65]
The 1973 oil crisis created a recession that hurt the automotive industry in Indiana. Companies such as Delco Electronics and Delphi began a long series of downsizing that contributed to high unemployment rates in manufacturing in Anderson, Muncie, and Kokomo. The restructuring and deindustrialization trend continued until the 1980s when the national and state economy began to diversify and recover.[66]
Geography

With a total area (land and water) of 36,418 square miles (94,320 km2), Indiana ranks as the 38th largest state in size.[67] The state has a maximum dimension north to south of 250 miles (400 km) and a maximum east to west dimension of 145 miles (233 km).[68] The state's geographic center (39° 53.7'N, 86° 16.0W) is in Marion County.[69]
Located in the Midwestern United States, Indiana is one of eight states that make up the Great Lakes Region.[70] Indiana is bordered on the north by Michigan, on the east by Ohio, and on the west by Illinois, partially separated by the Wabash River.[71] Lake Michigan borders Indiana on the northwest and the Ohio River separates Indiana from Kentucky on the south.[69][72]
Geology and terrain

The average altitude of Indiana is about 760 feet (230 m) above sea level.[73] The highest point in the state is Hoosier Hill in Wayne County at 1,257 feet (383 m) above sea level.[67][74] The lowest point at 320 feet (98 m) above sea level is in Posey County, where the Wabash River meets the Ohio River.[67][69] The resulting elevation span, 937 feet (286 m), is the narrowest of any non-coastal U.S. state. Only 2,850 square miles (7,400 km2) have an altitude greater than 1,000 feet (300 m) and this area is enclosed within 14 counties. About 4,700 square miles (12,000 km2) have an elevation of less than 500 feet (150 m), mostly concentrated along the Ohio and lower Wabash Valleys, from Tell City and Terre Haute to Evansville and Mount Vernon.[75]
The state includes two natural regions of the United States: the Central Lowlands and the Interior Low Plateaus.[76] The till plains make up the northern and central regions of Indiana. Much of its appearance is a result of elements left behind by glaciers. Central Indiana is mainly flat with some low rolling hills (except where rivers cut deep valleys through the plain, like at the Wabash River and Sugar Creek) and soil composed of glacial sands, gravel and clay, which results in exceptional farmland.[71] Northern Indiana is similar, except for the presence of higher and hillier terminal moraines and hundreds of kettle lakes. In northwest Indiana there are various sand ridges and dunes, some reaching nearly 200 feet in height; most of them are at Indiana Dunes National Park. These are along the Lake Michigan shoreline and also inland to the Kankakee Outwash Plain.
Southern Indiana is characterized by valleys and rugged, hilly terrain, contrasting with much of the state. Here, bedrock is exposed at the surface. Because of the prevalent Indiana limestone, the area has many caves, caverns, and quarries.
Hydrology

Major river systems in Indiana include the Whitewater, White, Blue, Wabash, St. Joseph, and Maumee rivers.[77] According to the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, as of 2007, there were 65 rivers, streams, and creeks of environmental interest or scenic beauty, which included only a portion of an estimated 24,000 total river miles within the state.[78]
The Wabash River, which is the longest free-flowing river east of the Mississippi River, is the official river of Indiana.[79][80] At 475 miles (764 kilometers) in length, the river bisects the state from northeast to southwest, forming part of the state's border with Illinois, before converging with the Ohio River. The river has been the subject of several songs, such as "On the Banks of the Wabash, Far Away", "Wabash Cannonball", and "Back Home Again in Indiana".[81][82]
There are about 900 lakes listed by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources.[83] To the northwest, Indiana borders Lake Michigan, one of five lakes comprising the Great Lakes, the largest group of freshwater lakes in the world. Tippecanoe Lake, the deepest lake in the state, reaches depths at nearly 120 feet (37 m), while Lake Wawasee is the largest natural lake in Indiana.[84] At 10,750 acres (summer pool level), Monroe Lake is the largest lake in Indiana.[85]
Climate

In the past, almost all of Indiana had a humid continental climate (Dfb), with cold winters and hot, wet summers;[86] only the extreme southern portion of the state lay within the humid subtropical climate (Cfa), which receives more precipitation than other parts of Indiana.[71] But as of the 2016 update, about half the state is now classified as humid subtropical. Temperatures generally diverge from the north and south sections of the state. In midwinter, average high/low temperatures range from around 30 °F/15 °F (−1 °C/−10 °C) in the far north to 41 °F/24 °F (5 °C/−4 °C) in the far south.[87]
In midsummer there is generally a little less variation across the state, as average high/low temperatures range from around 84 °F/64 °F (29 °C/18 °C) in the far north to 90 °F/69 °F (32 °C/21 °C) in the far south.[87] Indiana's record high temperature was 116 °F (47 °C) set on July 14, 1936, at Collegeville. The record low was −36 °F (−38 °C) on January 19, 1994 at New Whiteland.[88] The growing season typically spans from 155 days in the north to 185 days in the south.[citation needed]
While droughts occasionally occur in the state, rainfall totals are distributed relatively equally throughout the year. Precipitation totals range from 35 inches (89 cm) near Lake Michigan in northwest Indiana to 45 inches (110 cm) along the Ohio River in the south, while the state's average is 40 inches (100 cm). Annual snowfall in Indiana varies widely across the state, ranging from 80 inches (200 cm) in the northwest along Lake Michigan to 14 inches (36 cm) in the far south. Lake effect snow accounts for roughly half the snowfall in northwest and north central Indiana due to the effects of the moisture and relative warmth of Lake Michigan upwind. The mean wind speed is 8 miles per hour (13 km/h).[89]
In a 2012 report, Indiana was ranked eighth in a list of the top 20 tornado-prone states based on National Weather Service data from 1950 through 2011.[90] A 2011 report ranked South Bend 15th among the top 20 tornado-prone U.S. cities,[91] while another report from 2011 ranked Indianapolis eighth.[92][d][e]Despite its vulnerability, Indiana is not part of Tornado Alley.[93]