
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
 | |
| Continent | South America |
|---|---|
| Region | Caribbean |
| Coordinates | 8°00′N 66°00′W / 8.000°N 66.000°W |
| Area | Ranked 32nd |
| • Total | 912,050[1] km2 (352,140 sq mi) |
| • Land | 96.71% |
| • Water | 3.29% |
| Coastline | 2,800[1] km (1,700 mi) |
| Borders | 5,267 km (3,273 mi)[1] |
| Highest point | Pico Bolívar 4,978 m (16,332 ft)[1] |
| Lowest point | Caribbean Sea 0 metres (0 ft)[1] |
| Exclusive economic zone | 471,507 km2 (182,050 sq mi) |





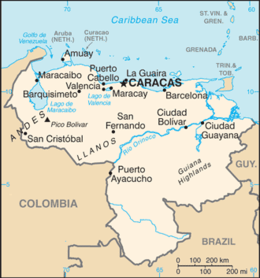
Venezuela is a country in South America, bordering the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, between Colombia and Guyana. It is situated on major sea and air routes linking North and South America. Located at the northernmost end of South America, Venezuela has a total area of 912,050 km2 (352,140 sq mi) and a land area of 882,050 km2 (340,560 sq mi).[2][1] It is the 32nd largest country and is slightly smaller than Egypt, or half the size of Mexico. Shaped roughly like an inverted triangle, the country has a 2,800 km (1,700 mi) long coastline.[2][1] It is bound on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the east by Guyana, on the south by Brazil, and on the west by Colombia.[2] It has the 55th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 471,507 km2 (182,050 sq mi). Its maritime territory borders Trinidad and Tobago, Dominica, the Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and the United States. The Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute has continued since the nineteenth century, with Venezuelan claiming a territory it calls "Guayana Esequiba", which is currently controlled by Guyana.
Topography
Most observers describe Venezuela in terms of four fairly well-defined regions: the Maracaibo lowlands in the northwest, the northern mountains extending in a broad east–west arc from the Colombian border along the Caribbean Sea, the wide Orinoco plains (Llanos) in central Venezuela, and rank highly dissected Guiana highlands in the southeast.[2]
The Maracaibo lowlands form a large spoon-shaped oval bounded by mountains on three sides and open to the Caribbean on the north.[2] The area is remarkably flat with only a gentle slope toward the center and away from the mountains that border the region.[2] Lake Maracaibo occupies much of the lower-lying territory.[2] Areas around the southern part of Lake Maracaibo are swampy, and, despite the rich agricultural land and significant petroleum deposits, the area was still thinly populated as of 1990.[2][needs update]
The mountains bordering the Caribbean Sea are actually the northeasternmost extension of the Andes chain.[2] Broken by several gaps, these high mountains have peaks over 4,500 metres (14,800 ft); the fertile valleys between the ranges contain most of Venezuela's population, industry, and agriculture.[2] The discontinuous westernmost range runs along the Colombian border and is the least densely populated part of this region.[2] The ranges southeast of Lake Maracaibo contain some of the highest peaks in the country (Pico Bolivar reaches 4,978 m (16,332 ft)), a few of which are snowcapped year-round.[2][1]
A broad gap separates this mountainous area from another rugged pair of ranges that parallel the north-central coast.[2] The series of valleys between these two parallel ranges constitute the core area of the country; as the site of burgeoning metropolitan Caracas, this comparatively small area hosts the country's densest population, the most intensive agriculture, and the best transportation network.[2] Another broad gap separates this area from the easternmost group of mountains, a series of dissected hills and uplands that rise steeply from the Caribbean and extend eastward almost to Trinidad.[2]
The great expanse of lowlands known as the Orinoco plains extend westward from the Caribbean coast to the Colombian border between the northern mountains and the Rio Orinoco.[2] This region is commonly known as the llanos, although it also contains large stretches of swampland in the Orinoco Delta and near the Colombian border.[2] The area slopes gradually away from the highland areas that surround it; elevations in the llanos never exceed 200 metres (660 ft).[2] North of the Rio Apure, rivers flowing out of the northern mountains cut shallow valleys, leaving eroded ridges that give the land a gently rolling appearance.[2] South of the Apure, the terrain is flatter and elevations lower.[2]
One of the oldest landforms in South America, the Guiana highlands rise almost immediately south and east of the Rio Orinoco.[2] Erosion has created unusual formations in this region.[2] Making up over half of the country, the highlands consist primarily of plateau areas scored by swiftly running tributaries of the Orinoco.[2] The most conspicuous topographical feature of the region is the Gran Sabana, a large, deeply eroded high plateau that rises from surrounding areas in abrupt cliffs up to 800 metres (2,600 ft).[2] Above the rolling surface of the Gran Sabana, massive, flat-topped bluffs emerge; many of these bluffs (referred to as tepuis by the Venezuelans) reach considerable altitudes.[2] The most famous tepui contains Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall.[2]
Climate
Although the country lies wholly within the tropics, its climate varies from tropical humid to alpine, depending on the elevation, topography, and the direction and intensity of prevailing winds.[2] Seasonal variations are marked less by temperature than by rainfall.[2] Most of the country has a distinct rainy season; the rainy period (May through November) is commonly referred to as winter and the remainder of the year as summer.[2]
Average yearly rainfall amounts in the lowlands and plains range from an arid 180 mm (7 in) in the Paraguaná Peninsula – the driest part of South America outside the Arid Diagonal[citation needed] – to around 1,000 mm (39 in) in the Orinoco Delta[2] and 2,200 mm (87 in) or more in Los Llanos and Amazonas.[citation needed] Rainfall in mountainous areas varies considerably; sheltered valleys receive little rain, but slopes exposed to the northeast trade winds experience heavy rainfall.[2] Caracas averages 800 mm (31 in) of precipitation annually, with very little rain falling from December to April.[2][3]
The country falls into four temperature zones based primarily on elevation. In the tropical zone—below 800 m (2,600 ft)—temperatures are hot, with yearly averages ranging between 26 and 28 °C (79 and 82 °F).[2] The temperate zone ranges between 800 and 2,000 m (2,600 and 6,600 ft) with averages from 12 to 25 °C (54 to 77 °F); many of Venezuela's cities, including the capital, lie in this region.[2] Colder conditions with temperatures from 9 to 11 °C (48 to 52 °F) are found in the cool zone between 2,000 and 3,000 m (6,600 and 9,800 ft).[2] Pastureland and permanent snowfield with yearly averages below 8 °C (46 °F) cover land above 3,000 m (9,800 ft) in the high mountain areas known as the páramos.[2]
Climate data
| Climate data for Caracas (Köppen Aw/Cwb) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.9 (89.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
33.5 (92.3) |
34.4 (93.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.6 (92.5) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.8 (87.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 23.3 (73.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.0 (77.0) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.6 (76.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.9 (76.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 19.6 (67.3) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
21.2 (70.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.2 (68.4) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 15.9 (60.6) |
15.8 (60.4) |
16.0 (60.8) |
17.5 (63.5) |
18.2 (64.8) |
18.1 (64.6) |
17.9 (64.2) |
18.1 (64.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
16.5 (61.7) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 7.1 (44.8) |
10.9 (51.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
12.5 (54.5) |
13.1 (55.6) |
14.9 (58.8) |
14.1 (57.4) |
14.3 (57.7) |
15.5 (59.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
11.9 (53.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 15.3 (0.60) |
13.2 (0.52) |
11.4 (0.45) |
59.2 (2.33) |
81.7 (3.22) |
134.1 (5.28) |
118.4 (4.66) |
123.8 (4.87) |
115.4 (4.54) |
126.3 (4.97) |
72.6 (2.86) |
41.4 (1.63) |
912.8 (35.94) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 19 | 19 | 18 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 10 | 142 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 73.7 | 74.2 | 73.0 | 76.3 | 75.4 | 75.1 | 74.1 | 74.0 | 74.9 | 74.7 | 73.7 | 74.7 | 74.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 229.4 | 217.5 | 235.6 | 183.0 | 182.9 | 183.0 | 210.8 | 217.0 | 213.0 | 210.8 | 210.0 | 213.9 | 2,506.9 |
| Source 1: Instituto Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología (INAMEH)[4][5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: World Meteorological Organization (rainfall data),[6] Hong Kong Observatory (sun only),[7] NOAA(extremes)[8] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Maracaibo (Köppen BSh/Aw) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 36.4 (97.5) |
39.4 (102.9) |
39.9 (103.8) |
39.6 (103.3) |
46.8 (116.2) |
39.0 (102.2) |
39.8 (103.6) |
38.1 (100.6) |
37.0 (98.6) |
36.6 (97.9) |
36.3 (97.3) |
36.8 (98.2) |
43.6 (110.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.5 (90.5) |
32.8 (91.0) |
33.1 (91.6) |
33.1 (91.6) |
33.1 (91.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
36.1 (97.0) |
35.2 (95.4) |
33.6 (92.5) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.5 (90.5) |
35.1 (95.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.7 (81.9) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.6 (85.3) |
29.1 (84.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.7 (83.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22.8 (73.0) |
23.2 (73.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.0 (77.0) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.6 (76.3) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.2 (75.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 19.2 (66.6) |
18.8 (65.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.2 (68.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
18.9 (66.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 5.1 (0.20) |
2.7 (0.11) |
5.9 (0.23) |
52.1 (2.05) |
66.8 (2.63) |
55.4 (2.18) |
26.5 (1.04) |
60.0 (2.36) |
104.0 (4.09) |
114.4 (4.50) |
70.6 (2.78) |
16.9 (0.67) |
580.4 (22.85) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 3.6 | 5.8 | 8.1 | 9.2 | 5.3 | 1.7 | 51.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.0 | 68.5 | 68.0 | 71.5 | 73.5 | 71.0 | 69.0 | 69.5 | 72.0 | 75.0 | 73.0 | 72.0 | 71.0 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 300.0 | 279.0 | 286.0 | 257.0 | 243.0 | 253.0 | 301.0 | 279.0 | 272.5 | 282.9 | 258.0 | 272.7 | 3,284.1 |
| Source 1: Instituto Nacional de Meteorología e Hidrología (INAMEH)[9][10] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (extremes and sun 1961–1990),[11] World Meteorological Organization (precipitation, 1961–1990)[12] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Valencia (Köppen Aw) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32 (90) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30.8 (87.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 21 (70) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21 (70) |
21.4 (70.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 7.9 (0.31) |
5.8 (0.23) |
12.0 (0.47) |
56.4 (2.22) |
79.2 (3.12) |
85.0 (3.35) |
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Geography_of_Venezuela|||||||
