A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article possibly contains original research. (April 2014) |
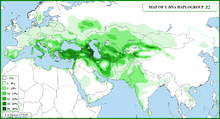
In human genetics, Haplogroup J-M172 or J2[Phylogenetics 1] is a Y-chromosome haplogroup which is a subclade (branch) of haplogroup J-M304.[Phylogenetics 2] Haplogroup J-M172 is common in modern populations in Western Asia, Central Asia, South Asia, Southern Europe, Northwestern Iran and North Africa. It is thought that J-M172 may have originated in the Caucasus, Anatolia and/or Western Iran.[9][10]
It is further divided into two complementary clades, J-M410 and J-M12 (M12, M102, M221, M314).
Origins
The date of origin for haplogroup J-M172 was estimated by Batini et al in 2015 as between 19,000 and 24,000 years before present (BP).[11] Samino et al in 2004 dated the origin of the parent haplogroup, J-P209, to between 18,900 and 44,500 YBP.[12] Ancient J-M410, specifically subclade J-Y12379*, has been found, in a mesolithic context, in a tooth from the Kotias Klde Cave in western Georgia dating 9.529-9.895 cal. BP.[13] This sample has been assigned to the Caucasus hunter-gatherers (CHG) autosomal component.[14] J-M410, more specifically its subclade J-PF5008, has also been found in a mesolithic sample from the Hotu and Kamarband Caves located in Mazandaran Province of Iran, dating back to 9,100-8,600 B.C.E (approximately 11,000 ybp).[15] Both samples belong to the Trialetian Culture. It is likely that J2 men had settled over most of Anatolia, the South Caucasus and the Zagros mountains by the end of the Last Glaciation 12,000 years ago.[16]
Zalloua and Wells 2004 and al-Zaheri 2003 claimed to have uncovered the earliest known migration of J2, expanded possibly from Anatolia and the Caucasus.[9][10][17] In 2001, Nebel et al. found that, "According to Underhill et al. (2000), Eu 9 (H58) evolved from Eu 10 (H71) through a T→G transversion at M172 (emphasis added)," and that in today's populations, Eu 9 (the post-mutation form of M172) is strongest in the Caucasus, Asia Minor and the Levant, whilst Eu 10 becomes stronger and replaces the frequency of Eu 9 as one moves south into the Arabian Peninsula,[18] so that people from the Caucasus met with Arabs near and between Mesopotamia (Sumer/Assyria) and the Negev Desert, as "Arabisation" spread from Arabia to the Fertile Crescent and Turkey.
Per research by Di Giacomo 2004, J-M172 haplogroup spread into Southern Europe from either the Levant or Anatolia, likely parallel to the development of agriculture.[19] As to the timing of its spread into Europe, Di Giacomo points to events which post-date the Neolithic, in particular the demographic floruit associated with the rise of the Ancient Greek world. Semino et al. derived older age estimates for overall J2 (having used the Zhivotovsky method c.f. Di Giacomo), postulating its initial spread with Neolithic farmers from the Near East. However, its subclade distribution, showing localized peaks in the Southern Balkans, southern Italy, north/central Italy and the Caucasus, does not conform to a single 'wave-of-advance' scenario, betraying a number of still poorly understood post-Neolithic processes which created its current pattern. Like Di Giacomo, the Bronze Age southern Balkans was suggested by Semino 2004 to have been an important vector of spread.[12]
Distribution
Haplogroup J-M172 is found mainly in the Fertile Crescent, the Caucasus (Nasidze 2003), Anatolia, Italy, the Mediterranean littoral, and the Iranian plateau (Semino 2004). Y-DNA: J2 (J-M172): Syrid/Nahrainid Arabid(s).
The highest reported frequency of J-M172 ever was 87.4%, among Ingush in Malgobek (Balanovsky 2011).
More specifically it is found in Iraq (Al-Zahery 2003), Kuwait,[20] Syria (Luis 2004), Lebanon (Zalloua 2008l), Turkey (Cinnioglu 2004), Georgia (Nasidze 2003), Azerbaijan (Di Giacomo 2004), North Caucasus (Nasidze 2004), Armenia (Wells 2001), Iran (Nasidze 2004), Israel (Semino 2004), Palestine (Semino 2004), Cyprus (Capelli 2005), Greece (Martinez 2007), Albania (Semino 2000), Italy (Capelli 2007), Spain (Di Giacomo 2003), and more frequently in Iraqis 24% (Al-Zahery 2011), Chechens 51.0%-58.0% (Balanovsky 2011), Georgians 21% (Wells 2001)-72% (Wells 2001), Lebanese 30% (Semino 2004), Ossetians 24% (Nasidze 2004), Balkars 24% (Battaglia 2008), Syrians 23% (Luis 2004), Turks 13% (Cinnioglu 2004)-40% (Semino 2000), Cypriots 12.9% (El-Sibai 2009)-37% (Capelli 2005), Armenians 21% (Wells 2001)-24% (Nasidze 2004), Circassians 21.8%(Balanovsky 2011), Iranians 10% (Nasidze 2004)-25% (Wells 2001), Albanians 16% (Battaglia 2008) and (Semino 2000), Italians 9%-36% (Capelli 2007), Sephardi Jews 15% (Nebel 2001)-29%(Semino 2004), Maltese 21% (Capelli 2005), Palestinians 17% (Semino 2004), Saudis 14% (Abu-Amero 2009), Jordanians 14%, Omanis 10%-15% (Di Giacomo 2004) and (Luis 2004) and North Indian Shia Muslim 18% (Eaaswarkhanth 2009).
North Africa
Haplogroup J2 is found with low frequencies in North Africa. with a hotspot in Sousse region Fadhlaoui-Zid 2014 most of Sousse samples have the same haplotypes found in Haplogroup J-L271 which was found in Msaken.
| Country/Region | Sampling | N | J-M172 | Study |
| Tunisia | Tunisia | 62 | 8 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Tunisia | Sousse | 220 | 8.2 | Fadhlaoui-Zid 2014 |
| Algeria | Oran | 102 | 4.9 | Robino 2008 |
| Egypt | 124 | 7.6 | El-Sibai 2009 | |
| Egypt | 147 | 12.0 | Abu-Amero 2009 | |
| Morocco | 221 | 4.1 | Fregel 2009 | |
| North Africa | Algeria, Tunisia | 202 | 3.5 | Fregel 2009 |
Central Asia
| Country/Region | Sampling | N | J-M172 | Study |
| Xinjiang | Lop Uyghurs | 64 | 57.8 | Liu 2018 |
| Xinjiang | Uyghurs | 50 | 34 | Shou 2010 |
| Tajikistan | Yaghnobis | 31 | 32 | Wells 2001 |
| Dushanbe | Tajiks | 16 | 31 | Wells 2001 |
| Xinjiang | Uzbeks | 23 | 30.4 | Shou 2010 |
| Afghanistan | Hazara | 60 | 26.6 | Haber 2012 |
| Xinjiang | Keriyan Uyghurs | 39 | 25.6 | Liu 2018 |
| Kazakhstan | Uyghurs | 41 | 20 | Wells 2001 |
| Samarkand | Tajiks | 40 | 20 | Wells 2001 |
| Tajikistan | Tajiks | 38 | 18.4 | Wells 2001 |
| Turkmenistan | Turkmens | 30 | 17 | Wells 2001 |
| Xinjiang | Pamiri Tajiks | 31 | 16.1 | Shou 2010 |
| Afghanistan | Uzbeks | 126 | 16 | Di Cristofaro 2013 |
| Bukhara | Uzbeks | 58 | 16 | Wells 2001 |
| Samarkand | Uzbeks | 45 | 16 | Wells 2001 |
| Surkhandarya | Uzbeks | 68 | 16 | Wells 2001 |
| Uzbekistan | Uzbeks | 366 | 13.4 | Wells 2001 |
| Kazakhstan | Kazakhs | 30 | 13.3 | Karafet 2001 |
| Turpan area | Uyghurs | 143 | 9.8 | [citation needed] |
| Hotan area | Uyghurs | 478 | 9.2 | [citation needed] |
| Changji | Hui | 175 | 9.1 | [citation needed] |
| Xinjiang | Dolan Uyghurs | 76 | 7.9 | Liu 2018 |
| Ningxia | Hui | 65 | 7.7 | [citation needed] |
| Kizilsu | Kyrgyz | 241 | 6.64% | Guo 2020 |
| Kazakhstan | Kazakhs | 1294 | 4.33% | Ashirbekov 2017 |
| Kyrgyzstan | Kyrgyz | 132 | 3.79% | Di Cristofaro 2013 |
J-M172 is found at moderate frequencies among Central Asian people such as Uyghurs, Uzbeks, Turkmens, Tajiks, Kazakhs, and Yaghnobis. According to the genetic study in Northwest China by Shou et al. (2010), a notable high frequency of J-M172 is observed particularly in Uyghurs 34% and Uzbeks 30.4% in Xinjiang, China. Liu Shuhu et al. (2018) found J2a1 (L26/Page55/PF5110/S57, L27/PF5111/S396) in 43.75% (28/64) and J2a2 (L581/S398) in 14.06% (9/64) of a sample of Lop Uyghurs from Qarchugha Village of Yuli (Lopnur) County, Xinjiang, J2a1b1 (M92, M260/Page14) in 25.64% (10/39) of a sample of Keriyan Uyghurs from Darya Boyi Village of Yutian (Keriya) County, Xinjiang, and J2a1 (L26/Page55/PF5110/S57, L27/PF5111/S396) in 3.95% (3/76) and J2a2 (L581/S398) in 3.95% (3/76) of a sample of Dolan Uyghurs from Horiqol Township of Awat County, Xinjiang.[21] Only far northwestern ethnic minorities had haplogroup J in Xinjiang, China. Uzbeks in the sample had 30.4% J2-M172 and Tajiks of Xinjiang and Uyghurs also had it.[22]
The haplogroup has an ancient presence in Central Asia and seems to have preceded the spread of Islam (Shou 2010). In addition, the immediate ancestor of J-M172, namely J* (J-M304*, a.k.a. J-P209*, J-12f2.1*) is also found among Xibo, Kazakh, Dongxiang and Uzbek people in Northwest China.
In 2015, two ancient samples belonging to J-M172 or J-M410 (J2a) were found at two different archaeological sites in Altai, eastern Russia: Kytmanovo and Sary-bel kurgan. Both of the ancient samples are related to Iron Age cultures in Altai. Sary-bel J2/J2a is dated to 50 BC whereas Kytmanovo sample is dated to 721-889 AD. Genetic admixture analysis of these samples also suggests that the individuals were more closely related to West Eurasians than other Altaians from the same period, although they also seem to be related to present-day Turkic peoples of the region.[23][24][25]
Europe
| Country/Region | Sampling | N | J-M172 | Study |
| Albania | 55 | 19.9% 11/55 |
Battaglia 2009 | |
| Bosnia-Herzegovina | Serbs | 81 | 8.7 | Battaglia 2009 |
| Cyprus | 164 | 12.9 | El-Sibai 2009 | |
| Greece | Crete | 143 | 35 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Iberia | 655 | 7 | Fregel 2009 | |
| Iberia | 1140 | 7.7 | Adams 2008 | |
| Italy | Sicily | 212 | 22.6 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Italy | Mainland | 699 | 20 | Capelli 2007 |
| Italy | Central Marche | 59 | 35.6 | Capelli 2007 |
| Italy | West Calabria | 57 | 35.1 | Capelli 2007 |
| Italy | Val Badia | 34 | 8.8 | Capelli 2007 |
| Malta | 90 | 21.1 | El-Sibai 2009 | |
| Portugal | North, Center, South | 303 | 6.9 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Portugal | Tras-os-Montes (Jews) | 57 | 24.5 | Nogueiro 2010 |
| Sardinia | 81 | 9.9 | El-Sibai 2009 | |
| Spain | Mallorca | 62 | 8.1 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Spain | Sevilla | 155 | 7.8 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Spain | Leon | 60 | 5 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Spain | Ibiza | 54 | 3.7 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Spain | Cantabria | 70 | 2.9 | El-Sibai 2009 |
| Spain | Galicia | 292 | 13 | [citation needed] |