
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
New Orleans
La Nouvelle-Orléans (French) | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Nickname(s): "The Crescent City", "The Big Easy", "The City That Care Forgot", "NOLA", "The City of Yes", "Hollywood South", "The Creole City" | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Louisiana | |
| Coordinates: 29°58′34″N 90°4′42″W / 29.97611°N 90.07833°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Louisiana |
| Parish | Orleans |
| Founded | 1718 |
| Founded by | Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville |
| Named for | Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (1674–1723) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Mayor | LaToya Cantrell (D) |
| • Council | New Orleans City Council |
| Area | |
| • Consolidated city-parish | 349.85 sq mi (906.10 km2) |
| • Land | 169.42 sq mi (438.80 km2) |
| • Water | 180.43 sq mi (467.30 km2) |
| • Metro | 3,755.2 sq mi (9,726.6 km2) |
| Elevation | −6.5 to 20 ft (−2 to 6 m) |
| Population | |
| • Consolidated city-parish | 383,997 |
| • Density | 2,267/sq mi (875/km2) |
| • Urban | 963,212 (US: 49th) |
| • Urban density | 3,563.8/sq mi (1,376.0/km2) |
| • Metro | 1,270,530 (US: 45th) |
| Demonym | New Orleanian |
| GDP | |
| • Consolidated city-parish | $29.147 billion (2022) |
| • MSA | $94.031 billion (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Area code | 504 |
| FIPS code | 22-55000 |
| GNIS feature ID | 1629985 |
| Website | nola |
New Orleans[a] (commonly known as NOLA or the Big Easy among other nicknames) is a consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 according to the 2020 U.S. census,[8] it is the most populous city in Louisiana and the French Louisiana region;[9] third most populous city in the Deep South; and the twelfth-most populous city in the southeastern United States. Serving as a major port, New Orleans is considered an economic and commercial hub for the broader Gulf Coast region of the United States.
New Orleans is world-renowned for its distinctive music, Creole cuisine, unique dialects, and its annual celebrations and festivals, most notably Mardi Gras. The historic heart of the city is the French Quarter, known for its French and Spanish Creole architecture and vibrant nightlife along Bourbon Street. The city has been described as the "most unique" in the United States,[10][11][12][13] owing in large part to its cross-cultural and multilingual heritage.[14] Additionally, New Orleans has increasingly been known as "Hollywood South" due to its prominent role in the film industry and in pop culture.[15][16]
Founded in 1718 by French colonists, New Orleans was once the territorial capital of French Louisiana before becoming part of the United States in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. New Orleans in 1840 was the third most populous city in the United States,[17] and it was the largest city in the American South from the Antebellum era until after World War II. The city has historically been very vulnerable to flooding, due to its high rainfall, low lying elevation, poor natural drainage, and proximity to multiple bodies of water. State and federal authorities have installed a complex system of levees and drainage pumps in an effort to protect the city.[18][19]
New Orleans was severely affected by Hurricane Katrina in late August 2005, which flooded more than 80% of the city, killed more than 1,800 people, and displaced thousands of residents, causing a population decline of over 50%.[20] Since Katrina, major redevelopment efforts have led to a rebound in the city's population. Concerns have been expressed about gentrification, new residents buying property in formerly close-knit communities, and displacement of longtime residents.[21][22][23][24] Additionally, high rates of violent crime continue to plague the city with New Orleans experiencing 280 murders in 2022, resulting in the highest per capita homicide rate in the United States.[25][26]
The city and Orleans Parish (French: paroisse d'Orléans) are coterminous.[27] As of 2017, Orleans Parish is the third most populous parish in Louisiana, behind East Baton Rouge Parish and neighboring Jefferson Parish.[28] The city and parish are bounded by St. Tammany Parish and Lake Pontchartrain to the north, St. Bernard Parish and Lake Borgne to the east, Plaquemines Parish to the south, and Jefferson Parish to the south and west.
The city anchors the larger Greater New Orleans metropolitan area, which had a population of 1,271,845 in 2020.[29] Greater New Orleans is the most populous metropolitan statistical area (MSA) in Louisiana and, since the 2020 census, has been the 46th most populous MSA in the United States.[30]
Etymology and nicknames

The name of New Orleans derives from the original French name (La Nouvelle-Orléans), which was given to the city in honor of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, who served as Louis XV's regent from 1715 to 1723.[31] The French city of Orléans itself is named after the Roman emperor Aurelian, originally being known as Aurelianum. Thus, by extension, since New Orleans is also named after Aurelian, its name in Latin would translate to Nova Aurelia.
Following France's defeat in the Seven Years' War and the Treaty of Paris, which was signed in 1763, France transferred possession of Louisiana to Spain. The Spanish renamed the city to Nueva Orleans (pronounced [ˌnweβa oɾleˈans]), which was used until 1800.[32] When the United States acquired possession from France in 1803, the French name was adopted and anglicized to become the modern name, which is still in use today.
New Orleans has several nicknames, including these:
- Crescent City, alluding to the course of the Lower Mississippi River around and through the city.[33]
- The Big Easy, possibly a reference by musicians in the early 20th century to the relative ease of finding work there.[34][35]
- The City that Care Forgot, used since at least 1938,[36] referring to the outwardly easygoing, carefree nature of the residents.[35]
- NOLA, the acronym for New Orleans, Louisiana.
History
French–Spanish colonial era
Kingdom of France 1718–1763
Kingdom of Spain 1763–1802
French First Republic 1802–1803
United States of America 1803–1861
State of Louisiana 1861
Confederate States of America 1861–1862
United States of America 1862–present
La Nouvelle-Orléans (New Orleans) was founded in the spring of 1718 (May 7 has become the traditional date to mark the anniversary, but the actual day is unknown)[37] by the French Mississippi Company, under the direction of Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville, on land inhabited by the Chitimacha. It was named for Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, who was regent of the Kingdom of France at the time.[31] His title came from the French city of Orléans. The French colony of Louisiana was ceded to the Spanish Empire in the 1763 Treaty of Paris, following France's defeat by Great Britain in the Seven Years' War. During the American Revolutionary War, New Orleans was an important port for smuggling aid to the American revolutionaries, and transporting military equipment and supplies up the Mississippi River. Beginning in the 1760s, Filipinos began to settle in and around New Orleans.[38] Bernardo de Gálvez y Madrid, Count of Gálvez successfully directed a southern campaign against the British from the city in 1779.[39] Nueva Orleans (the name of New Orleans in Spanish)[40] remained under Spanish control until 1803, when it reverted briefly to French rule. Nearly all of the surviving 18th-century architecture of the Vieux Carré (French Quarter) dates from the Spanish period, notably excepting the Old Ursuline Convent.[41]

As a French colony, Louisiana faced struggles with numerous Native American tribes, who were navigating the competing interests of France, Spain, and England, as well as traditional rivals. Notably, the Natchez, whose traditional lands were along the Mississippi near the modern city of Natchez, Mississippi, had a series of wars culminating in the Natchez Revolt that began in 1729 with the Natchez overrunning Fort Rosalie. Approximately 230 French colonists were killed and the Natchez settlement destroyed, causing fear and concern in New Orleans and the rest of the territory.[42] In retaliation, then-governor Étienne Perier launched a campaign to completely destroy the Natchez nation and its Native allies.[43] By 1731, the Natchez people had been killed, enslaved, or dispersed among other tribes, but the campaign soured relations between France and the territory's Native Americans leading directly into the Chickasaw Wars of the 1730s.[44]
Relations with Louisiana's Native American population remained a concern into the 1740s for governor Marquis de Vaudreuil. In the early 1740s traders from the Thirteen Colonies crossed into the Appalachian Mountains. The Native American tribes would now operate dependent on which of various European colonists would most benefit them. Several of these tribes and especially the Chickasaw and Choctaw would trade goods and gifts for their loyalty.[45] The economic issue in the colony, which continued under Vaudreuil, resulted in many raids by Native American tribes, taking advantage of the French weakness. In 1747 and 1748, the Chickasaw would raid along the east bank of the Mississippi all the way south to Baton Rouge. These raids would often force residents of French Louisiana to take refuge in New Orleans proper.
Inability to find labor was the most pressing issue in the young colony. The colonists turned to sub-Saharan African slaves to make their investments in Louisiana profitable. In the late 1710s the transatlantic slave trade imported enslaved Africans into the colony. This led to the biggest shipment in 1716 where several trading ships appeared with slaves as cargo to the local residents in a one-year span.
By 1724, the large number of blacks in Louisiana prompted the institutionalizing of laws governing slavery within the colony.[46] These laws required that slaves be baptized in the Roman Catholic faith, slaves be married in the church; the slave law formed in the 1720s is known as the Code Noir, which would bleed into the antebellum period of the American South as well. Louisiana slave culture had its own distinct Afro-Creole society that called on past cultures and the situation for slaves in the New World. Afro-Creole was present in religious beliefs and the Louisiana Creole language. The religion most associated with this period was called Voodoo.[47][48]
In the city of New Orleans an inspiring mixture of foreign influences created a melting pot of culture that is still celebrated today. By the end of French colonization in Louisiana, New Orleans was recognized commercially in the Atlantic world. Its inhabitants traded across the French commercial system. New Orleans was a hub for this trade both physically and culturally because it served as the exit point to the rest of the globe for the interior of the North American continent.
In one instance the French government established a chapter house of sisters in New Orleans. The Ursuline sisters after being sponsored by the Company of the Indies, founded a convent in the city in 1727.[49] At the end of the colonial era, the Ursuline Academy maintained a house of 70 boarding and 100 day students. Today numerous schools in New Orleans can trace their lineage from this academy.

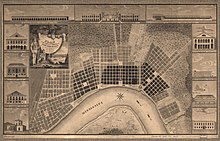
Another notable example is the street plan and architecture still distinguishing New Orleans today. French Louisiana had early architects in the province who were trained as military engineers and were now assigned to design government buildings. Pierre Le Blond de Tour and Adrien de Pauger, for example, planned many early fortifications, along with the street plan for the city of New Orleans.[50] After them in the 1740s, Ignace François Broutin, as engineer-in-chief of Louisiana, reworked the architecture of New Orleans with an extensive public works program.
French policy-makers in Paris attempted to set political and economic norms for New Orleans. It acted autonomously in much of its cultural and physical aspects, but also stayed in communication with the foreign trends as well.
After the French relinquished West Louisiana to the Spanish, New Orleans merchants attempted to ignore Spanish rule and even re-institute French control on the colony. The citizens of New Orleans held a series of public meetings during 1765 to keep the populace in opposition of the establishment of Spanish rule. Anti-Spanish passions in New Orleans reached their highest level after two years of Spanish administration in Louisiana. On October 27, 1768, a mob of local residents, spiked the guns guarding New Orleans and took control of the city from the Spanish.[51] The rebellion organized a group to sail for Paris, where it met with officials of the French government. This group brought with them a long memorial to summarize the abuses the colony had endured from the Spanish. King Louis XV and his ministers reaffirmed Spain's sovereignty over Louisiana.
United States territorial era
The Third Treaty of San Ildefonso in 1800 restored French control of New Orleans and Louisiana, but Napoleon sold both to the United States in the Louisiana Purchase in 1803.[52] Thereafter, the city grew rapidly with influxes of Americans, French, Creoles and Africans. Later immigrants were Irish, Germans, Poles and Italians. Major commodity crops of sugar and cotton were cultivated with slave labor on nearby large plantations.
Between 1791 and 1810, thousands of St. Dominican refugees from the Haitian Revolution, both whites and free people of color (affranchis or gens de couleur libres), arrived in New Orleans; a number brought their slaves with them, many of whom were native Africans or of full-blood descent.[53] While Governor Claiborne and other officials wanted to keep out additional free black people, the French Creoles wanted to increase the French-speaking population. In addition to bolstering the territory's French-speaking population, these refugees had a significant impact on the culture of Louisiana, including developing its sugar industry and cultural institutions.[54]
As more refugees were allowed into the Territory of Orleans, St. Dominican refugees who had first gone to Cuba also arrived.[55] Many of the white Francophones had been deported by officials in Cuba in 1809 as retaliation for Bonapartist schemes.[56] Nearly 90 percent of these immigrants settled in New Orleans. The 1809 migration brought 2,731 whites, 3,102 free people of color (of mixed-race European and African descent), and 3,226 slaves of primarily African descent, doubling the city's population. The city became 63 percent black, a greater proportion than Charleston, South Carolina's 53 percent at that time.[55]
Battle of New Orleans

During the final campaign of the War of 1812, the British sent a force of 11,000 in an attempt to capture New Orleans. Despite great challenges, General Andrew Jackson, with support from the U.S. Navy, successfully cobbled together a force of militia from Louisiana and Mississippi, U.S. Army regulars, a large contingent of Tennessee state militia, Kentucky frontiersmen and local privateers (the latter led by the pirate Jean Lafitte), to decisively defeat the British, led by Sir Edward Pakenham, in the Battle of New Orleans on January 8, 1815.[58]
The armies had not learned of the Treaty of Ghent, which had been signed on December 24, 1814 (however, the treaty did not call for cessation of hostilities until after both governments had ratified it. The U.S. government ratified it on February 16, 1815). The fighting in Louisiana began in December 1814 and did not end until late January, after the Americans held off the Royal Navy during a ten-day siege of Fort St. Philip (the Royal Navy went on to capture Fort Bowyer near Mobile, before the commanders received news of the peace treaty).[58]
Port

As a port, New Orleans played a major role during the antebellum period in the Atlantic slave trade. The port handled commodities for export from the interior and imported goods from other countries, which were warehoused and transferred in New Orleans to smaller vessels and distributed along the Mississippi River watershed. The river was filled with steamboats, flatboats and sailing ships. Despite its role in the slave trade, New Orleans at the time also had the largest and most prosperous community of free persons of color in the nation, who were often educated, middle-class property owners.[59][60]
Dwarfing the other cities in the Antebellum South, New Orleans had the U.S.' largest slave market. The market expanded after the United States ended the international trade in 1808. Two-thirds of the more than one million slaves brought to the Deep South arrived via forced migration in the domestic slave trade. The money generated by the sale of slaves in the Upper South has been estimated at 15 percent of the value of the staple crop economy. The slaves were collectively valued at half a billion dollars. The trade spawned an ancillary economy—transportation, housing and clothing, fees, etc., estimated at 13.5 percent of the price per person, amounting to tens of billions of dollars (2005 dollars, adjusted for inflation) during the antebellum period, with New Orleans as a prime beneficiary.[61]
According to historian Paul Lachance,
the addition of white immigrants to the white creole population enabled French-speakers to remain a majority of the white population until almost 1830. If a substantial proportion of free persons of color and slaves had not also spoken French, however, the Gallic community would have become a minority of the total population as early as 1820.[62]
After the Louisiana Purchase, numerous Anglo-Americans migrated to the city. The population doubled in the 1830s and by 1840, New Orleans had become the nation's wealthiest and the third-most populous city, after New York and Baltimore.[63] German and Irish immigrants began arriving in the 1840s, working as port laborers. In this period, the state legislature passed more restrictions on manumissions of slaves and virtually ended it in 1852.[64]
In the 1850s, white Francophones remained an intact and vibrant community in New Orleans. They maintained instruction in French in two of the city's four school districts (all served white students).[65] In 1860, the city had 13,000 free people of color (gens de couleur libres), the class of free, mostly mixed-race people that expanded in number during French and Spanish rule. They set up some private schools for their children. The census recorded 81 percent of the free people of color as mulatto, a term used to cover all degrees of mixed race.[64][page needed] Mostly part of the Francophone group, they constituted the artisan, educated and professional class of African Americans. The mass of blacks were still enslaved, working at the port, in domestic service, in crafts, and mostly on the many large, surrounding sugarcane plantations.
Throughout New Orleans' history, until the early 20th century when medical and scientific advances ameliorated the situation, the city suffered repeated epidemics of yellow fever and other tropical and infectious diseases.[66] In the first half of the 19th century, yellow fever epidemics killed over 150,000 people in New Orleans.[67]
After growing by 45 percent in the 1850s, by 1860, the city had nearly 170,000 people.[68] It had grown in wealth, with a "per capita income was second in the nation and the highest in the South."[68] The city had a role as the "primary commercial gateway for the nation's booming midsection."[68] The port was the nation's third largest in terms of tonnage of imported goods, after Boston and New York, handling 659,000 tons in 1859.[68]
Civil War–Reconstruction era
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=City_of_New_OrleansText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk










