
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
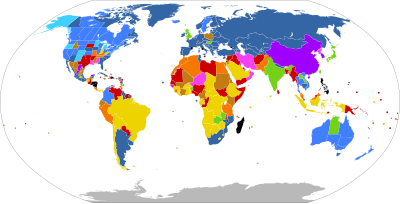
| Legal on request: | |
| No gestational limit | |
| Gestational limit after the first 17 weeks | |
| Gestational limit in the first 17 weeks | |
| Unclear gestational limit | |
| Legally restricted to cases of: | |
| Risk to woman's life, to her health*, rape*, fetal impairment*, or socioeconomic factors | |
| Risk to woman's life, to her health*, rape, or fetal impairment | |
| Risk to woman's life, to her health*, or fetal impairment | |
| Risk to woman's life*, to her health*, or rape | |
| Risk to woman's life or to her health | |
| Risk to woman's life | |
| Illegal with no exceptions | |
| No information | |
| * Does not apply to some countries or territories in that category | |
Abortion laws vary widely among countries and territories, and have changed over time. Such laws range from abortion being freely available on request, to regulation or restrictions of various kinds, to outright prohibition in all circumstances. Many countries and territories that allow abortion have gestational limits for the procedure depending on the reason; with the majority being up to 12 weeks for abortion on request, up to 24 weeks for rape, incest, or socioeconomic reasons, and more for fetal impairment or risk to the woman's health or life. As of 2022, countries that legally allow abortion on request or for socioeconomic reasons comprise about 60% of the world's population. In 2024, France became the first country to explicitly protect abortion rights in its constitution.[1]
Abortion continues to be a controversial subject in many societies on religious, moral, ethical, practical, and political grounds. Though it has been banned and otherwise limited by law in many jurisdictions, abortions continue to be common in many areas, even where they are illegal. According to a 2007 study conducted by the Guttmacher Institute and the World Health Organization, abortion rates are similar in countries where the procedure is legal and in countries where it is not,[2][3] due to unavailability of modern contraceptives in areas where abortion is illegal.[4] Also according to the study, the number of abortions worldwide is declining due to increased access to contraception.[2][3]
History
This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2017) |
Abortion has existed since ancient times, with natural abortifacients being found amongst a wide variety of tribal people and in most written sources. The earliest known records of abortion techniques and general reproductive regulation date as far back as 2700 BC in China, and 1550 BC in Egypt.[5] Early texts contain little mention of abortion or abortion law. When it does appear, it is entailed in concerns about male property rights, preservation of social order, and the duty to produce fit citizens for the state or community. The harshest penalties were generally reserved for a woman who procured an abortion against her husband's wishes, and for slaves who produced abortion in a woman of high status. Religious texts often contained severe condemnations of abortion, recommending penance but seldom enforcing secular punishment. As a matter of common law in England and the United States, abortion was illegal anytime after quickening—when the movements of the fetus could first be felt by the woman. Under the born alive rule, the fetus was not considered a "reasonable being" in rerum natura; and abortion was not treated as murder in English law.
In the 19th century, many Western countries began to codify abortion laws or place further restrictions on the practice. Anti-abortion movements were led by a combination of groups opposed to abortion on moral grounds, and by medical professionals who were concerned about the danger presented by the procedure and the regular involvement of non-medical personnel in performing abortions. Nevertheless, it became clear that illegal abortions continued to take place in large numbers even where abortions were rigorously restricted. It was difficult to obtain sufficient evidence to prosecute the women and abortion doctors, and judges and juries were often reluctant to convict. For example, Henry Morgentaler, a Canadian pro-choice advocate, was never convicted by a jury. He was acquitted by a jury in the 1973 court case, but the acquittal was overturned by five judges on the Quebec Court of Appeal in 1974. He went to prison, appealed, and was again acquitted. In total, he served 10 months, suffering a heart attack while in solitary confinement. Many were also outraged at the invasion of privacy and the medical problems resulting from abortions taking place illegally in medically dangerous circumstances. Political movements soon coalesced around the legalization of abortion and liberalization of existing laws.
By the first half of the 20th century, many countries had begun to liberalize abortion laws, at least when performed to protect the woman's life and in some cases on the woman's request. Under Vladimir Lenin, the Soviet Union became the first modern state in legalizing abortions on request—the law was first introduced in the Russian SFSR in 1920, in the Ukrainian SSR in July 1921, and then in the whole country.[6][7] The Bolsheviks saw abortion as a social evil created by the capitalist system, which left women without the economic means to raise children, forcing them to perform abortions. The Soviet state initially preserved the tsarist ban on abortion, which treated the practice as premeditated murder. However, abortion had been practiced by Russian women for decades and its incidence skyrocketed further as a result of the Russian Civil War, which had left the country economically devastated and made it extremely difficult for many people to have children. The Soviet state recognized that banning abortion would not stop the practice because women would continue using the services of private abortionists. In rural areas, these were often old women who had no medical training, which made their services very dangerous to women's health. In November 1920, the Soviet government legalized abortion in state hospitals. The state considered abortion as a temporary necessary evil, which would disappear in the future communist society, which would be able to provide for all the children conceived.[8][page needed] In 1936, Joseph Stalin placed prohibitions on abortions, which restricted them to medically recommended cases only, in order to increase population growth after the enormous loss of life in World War I and the Russian Civil War.[9][10][7] In the 1930s, several countries (Poland, Turkey, Denmark, Sweden, Iceland, Mexico) legalized abortion in some special cases (pregnancy from rape, threat to mother's health, fetal malformation). In Japan, abortion was legalized in 1948 by the Eugenic Protection Law,[11] amended in May 1949 to allow abortions for economic reasons.[12] Abortion was legalized in 1952 in Yugoslavia (on a limited basis[which?]), and again in 1955 in the Soviet Union on request. Some Soviet allies (Poland, Hungary, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Romania) legalized abortion in the late 1950s under pressure from the Soviets.[how?][13][additional citation(s) needed]
In the United Kingdom, the Abortion Act of 1967 clarified and prescribed abortions as legal up to 28 weeks (later reduced to 24 weeks). Other countries soon followed, including Canada (1969), the United States (1973 in most states, pursuant to Roe v. Wade—the U.S. Supreme Court decision which legalized abortion nationwide), Tunisia and Denmark (1973), Austria (1974), France and Sweden (1975), New Zealand (1977), Italy (1978), the Netherlands (1984), and Belgium (1990). However, these countries vary greatly in the circumstances under which abortion was to be permitted. In 1975, the West German Supreme Court struck down a law legalizing abortion, holding that they contradict the constitution's human rights guarantees. In 1976, a law was adopted which enabled abortions up to 12 weeks. After Germany's reunification, despite the legal status of abortion in former East Germany, a compromise was reached which deemed most abortions up to 12 weeks legal, but this law was struck down by the Federal Constitutional Court and amended to only remove the punishment in such cases, without any statement to legality. In jurisdictions governed under sharia law, abortion after the 120th day from conception (19 weeks from LMP) is illegal, especially for those who follow the recommendations of the Hanafi legal school, while most jurists of the Maliki legal school "believe that ensoulment occurs at the moment of conception, and they tend to forbid abortion at any point . The other schools hold intermediate positions. ... The penalty prescribed for an illegal abortion varies according to particular circumstances involved. According to sharia, it should be limited to a fine that is paid to the father or heirs of the fetus."[14]
Timeline of abortion on request
The table below lists in chronological order the United Nations member states that have legalized abortion on request in at least some initial part of the pregnancy, or that have fully decriminalized abortion. As of 2023, 67 countries have legalized or decriminalized abortion on request.
- Notes
Where a country has legalized abortion on request, prohibited it, and legalized it again (e.g., former Soviet Union, Romania), only the later year is included. Countries that result from the merger of states where abortion on request was legal at the moment of unification show the year when it became legal across the whole national territory (e.g., Germany, Vietnam). Similarly, countries where not all subnational jurisdictions have legalized abortion on request are not included, leading to the exclusion of Australia, Mexico, and the United Kingdom. Countries where abortion on request was once legalized nationwide but has since been prohibited in at least part of the country, such as the United States and Poland, are also excluded. Countries are counted even if they were not yet independent at the time. The year refers to when the relevant law or judicial decision came into force, which may be different from the year when it was approved.
International law
There are no international or multinational treaties that deal directly with abortion but human rights law and International criminal law touch on the issues.
The Nuremberg Military Tribunal decided the case of United States v Greifelt and Others (1948) on the basis that abortion was a crime within its jurisdiction according to the law defining crimes against humanity and thus within its definition of murder and extermination.[36]
The Catholic Church remains highly influential in Latin America, and opposes the legalisation of abortion.[37] The American Convention on Human Rights, which in 2013 had 23 Latin American parties, declares human life as commencing with conception. In Latin America, abortion on request is only legal in Cuba (1965), Uruguay (2012),[38] Argentina (2021),[35] Colombia (2022)[39] and in parts of Mexico.[40][41] Abortions are completely banned in the Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Honduras and Nicaragua, and only allowed in certain restricted circumstances in most other Latin American nations.[37]
In the 2010 case of A, B and C v Ireland, the European Court of Human Rights found that the European Convention on Human Rights did not include a right to an abortion.
In 2005, the United Nations Human Rights Committee (UN HRC) ordered Peru to compensate a woman (known as K.L.) for denying her a medically indicated abortion; this was the first time a United Nations Committee had held any country accountable for not ensuring access to safe, legal abortion, and the first time the committee affirmed that abortion is a human right.[42] K.L. received the compensation in 2016.[42] In the 2016 case of Mellet v Ireland, the UN HRC found Ireland's abortion laws violated International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights because Irish law banned abortion in cases of fatal fetal abnormalities.
National laws
While abortions are legal at least under certain conditions in almost all countries, these conditions vary widely. According to a United Nations (UN) report with data gathered up to 2019,[43] abortion is allowed in 98% of countries in order to save a woman's life. Other commonly-accepted reasons are preserving physical (72%) or mental health (69%), in cases of rape or incest (61%), and in cases of fetal impairment (61%). Performing an abortion because of economic or social reasons is accepted in 37% of countries. Performing abortion only on the basis of a woman's request is allowed in 34% of countries, including in Canada, most European countries and China.[43]
The exact scope of each legal ground also varies. For example, the laws of some countries cite health risks and fetal impairment as general grounds for abortion and allow a broad interpretation of such terms in practice, while other countries restrict them to a specific list of medical conditions or subcategories. Many countries that allow abortion have gestational limits for the procedure depending on the reason; with the majority being up to 12 weeks for abortion on request, up to 24 weeks for social, economic, rape, or incest reasons, and more for fetal impairment or threats to the woman's health or life.[43]: 26
In some countries, additional procedures must be followed before the abortion can be carried out even if the basic grounds for it are met. How strictly all of the procedures dictated in the legislation are followed in practice is another matter. For example, in the United Kingdom, a Care Quality Commission's report in 2012 found that several NHS clinics were circumventing the law, using forms pre-signed by one doctor, thus allowing abortions to patients who only met with one doctor.[44]
Roe V. Wade has been established in the US for almost 50 years, put into motion in 1973, before its overturn in 2022 due to Dobbs v. Jackson. This ruling made abortion access not a constitutional right. The decision, most of which was leaked in early May, means that abortion rights will be rolled back in nearly half of the states immediately, with more restrictions likely to follow. For all practical purposes, abortion will not be available in large swaths of the country. 13 States, Arkansas, Idaho, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, and Wyoming enacted a trigger law which placed an immediate but varying statewide abortion ban immediately following the overturning. These trigger laws were designed specifically to take effect immediately upon the fall of the Roe precedent. Other states, were bans are in effect after 6 weeks gestation, including Idaho, Tennessee, and Texas – have similar laws, which would take effect after 30 days of the overturning.[45]
Pill abortion access is legal in 36 states. However, a lawsuit in Texas is currently against the production and distribution of this Abortion pill, misoprostol. The ban would affect millions of women in the US who cannot access a medical procedural abortion due to a state ban. The group suing the FDA has asked for a preliminary injunction to take one of the two drugs used in a medication abortion, mifepristone, off the market while the case plays out. This will effectively cause a nationwide ban of pill abortion if granted.[46]
Summary tables
| permitted | In many cases, abortion is permitted only up to a certain gestational age. If this limit is known and does not vary by subdivision, it is shown instead of "permitted". |
| permitted, with complex legality or practice | |
| varies by subdivision | |
| prohibited, with complex legality or practice | |
| prohibited | |
| unknown or unclear |
Countries
The table below summarizes the legal grounds for abortion in all United Nations member states and United Nations General Assembly observer states and some countries with limited recognition. This table is mostly based on data compiled by the United Nations up to 2019,[47] with some updates, additions and clarifications citing other sources.
| Country | Risk to life | Risk to health | Rape | Fetal impairment | Economic or social | On request |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | |
| permitted[o] | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited[o] | prohibited[o] | prohibited | |
| 22 weeks | 22 weeks | 22 weeks | no limit | 22 weeks | 12 weeks | |
| permitted | permitted | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | |
| prohibited[p] | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | |
| permitted | permitted | 16 weeks | permitted | prohibited | prohibited | |
| permitted[r] | prohibited[s] | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | |
| no limit | no limit | no limit | 14 weeks | 14 weeks | 14 weeks | |
| permitted | permitted | permitted | permitted | 22 weeks | 12 weeks | |
| no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | varies[t] | |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 23 weeks |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 23 weeks |
| Jervis Bay Territory[w] | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 22 weeks |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | prohibited[y] |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 22 weeks |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 22 weeks and 6 days |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 16 weeks |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 24 weeks |
| |
no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | no limit | 23 weeks |
| no limit | no limit | 3 months[z] | no limit | 3 months[z] | 3 months[z] | |
| no limit | no limit | permitted | permitted | 22 weeks | 12 weeks | |
| permitted | permitted[aa] | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | prohibited | |
| permitted | prohibited[ab] | prohibited[ab] | prohibited[ab] | prohibited[ab] | prohibited[ab] | |
| no limit | prohibited[ac] | prohibited[ac] | prohibited[ac] | prohibited[ac] | prohibited[ac] | |
| no limit | no limit | 12 weeks | no limit | 12 weeks | prohibited | |
| no limit | no limit | 22 weeks | no limit | 22 weeks | 12 weeks | |
| no limit | no limit | 14 weeks[ae] | no limit | 14 weeks[ae] | 14 weeks[ae] | |
| no limit | no limit | prohibited | no limit | permitted | prohibited | |
| Country | Risk to life | Risk to health | Rape | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Abortion_law
