
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (June 2015) |

In mathematics, a divisor of an integer also called a factor of is an integer that may be multiplied by some integer to produce [1] In this case, one also says that is a multiple of An integer is divisible or evenly divisible by another integer if is a divisor of ; this implies dividing by leaves no remainder.
Definition
An integer is divisible by a nonzero integer if there exists an integer such that This is written as
This may be read as that divides is a divisor of is a factor of or is a multiple of If does not divide then the notation is [2][3]
There are two conventions, distinguished by whether is permitted to be zero:
- With the convention without an additional constraint on for every integer [2][3]
- With the convention that be nonzero, for every nonzero integer [4][5]
General
Divisors can be negative as well as positive, although often the term is restricted to positive divisors. For example, there are six divisors of 4; they are 1, 2, 4, −1, −2, and −4, but only the positive ones (1, 2, and 4) would usually be mentioned.
1 and −1 divide (are divisors of) every integer. Every integer (and its negation) is a divisor of itself. Integers divisible by 2 are called even, and integers not divisible by 2 are called odd.
1, −1, and are known as the trivial divisors of A divisor of that is not a trivial divisor is known as a non-trivial divisor (or strict divisor[6]). A nonzero integer with at least one non-trivial divisor is known as a composite number, while the units −1 and 1 and prime numbers have no non-trivial divisors.
There are divisibility rules that allow one to recognize certain divisors of a number from the number's digits.
Examples

- 7 is a divisor of 42 because so we can say It can also be said that 42 is divisible by 7, 42 is a multiple of 7, 7 divides 42, or 7 is a factor of 42.
- The non-trivial divisors of 6 are 2, −2, 3, −3.
- The positive divisors of 42 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, 42.
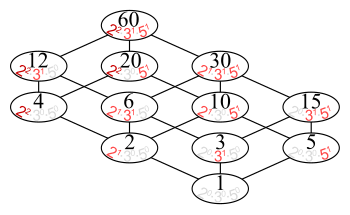
- The set of all positive divisors of 60, partially ordered by divisibility, has the Hasse diagram:
Further notions and facts
There are some elementary rules:
- If and then i.e. divisibility is a transitive relation.
- If and then or
- If and then holds, as does [a] However, if and then does not always hold (e.g. and but 5 does not divide 6).
If and then [b] This is called Euclid's lemma.
If is a prime number and
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk































