
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| Great white shark Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Male off Isla Guadalupe, Mexico | |
| |
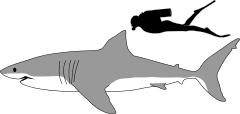
| Size comparison with human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Subdivision: | Selachimorpha |
| Order: | Lamniformes |
| Family: | Lamnidae |
| Genus: | Carcharodon A. Smith, 1838 |
| Species: | C. carcharias
|
| Binomial name | |
| Carcharodon carcharias | |
| |
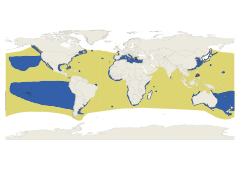
| Great white shark range according to the IUCN (2018)
Extant (resident)
Possibly extant (resident)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias), also known as the white shark, white pointer, or simply great white, is a species of large mackerel shark which can be found in the coastal surface waters of all the major oceans. It is the only known surviving species of its genus Carcharodon. The great white shark is notable for its size, with the largest preserved female specimen measuring 5.83 m (19.1 ft) in length and around 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) in weight at maturity.[3] However, most are smaller; males measure 3.4 to 4.0 m (11 to 13 ft), and females measure 4.6 to 4.9 m (15 to 16 ft) on average.[4][5] According to a 2014 study, the lifespan of great white sharks is estimated to be as long as 70 years or more, well above previous estimates,[6] making it one of the longest lived cartilaginous fishes currently known.[7] According to the same study, male great white sharks take 26 years to reach sexual maturity, while the females take 33 years to be ready to produce offspring.[8] Great white sharks can swim at speeds of 25 km/h (16 mph)[9] for short bursts and to depths of 1,200 m (3,900 ft).[10]
The great white shark is arguably the world's largest-known extant macropredatory fish, and is one of the primary predators of marine mammals, such as pinnipeds and dolphins. The great white shark is also known to prey upon a variety of other animals, including fish, other sharks, and seabirds. It has only one recorded natural predator, the orca.[11]
The species faces numerous ecological challenges which has resulted in international protection. The International Union for Conservation of Nature lists the great white shark as a vulnerable species,[1] and it is included in Appendix II of CITES.[12] It is also protected by several national governments, such as Australia (as of 2018).[13] Due to their need to travel long distances for seasonal migration and extremely demanding diet, it is not logistically feasible to keep great white sharks in captivity; because of this, while attempts have been made to do so in the past, there are no known aquariums in the world believed to house a live specimen.[14]
The great white shark is depicted in popular culture as a ferocious man-eater, largely as a result of the novel Jaws by Peter Benchley and its subsequent film adaptation by Steven Spielberg. Humans are not a preferred prey,[15] but nevertheless it is responsible for the largest number of reported and identified fatal unprovoked shark attacks on humans.[16] However, attacks are rare, typically occurring fewer than 10 times per year globally.[17][18]
Taxonomy
The great white is the sole recognized extant species in the genus Carcharodon, and is one of five extant species belonging to the family Lamnidae.[19] Other members of this family include the mako sharks, porbeagle, and salmon shark. The family belongs to the Lamniformes, the order of mackerel sharks.[20]
Etymology and naming history

The English name 'white shark' and its Australian variant 'white pointer'[21] is thought to have come from the shark's stark white underside, a characteristic feature most noticeable in beached sharks lying upside down with their bellies exposed.[22] Colloquial use favours the name 'great white shark', with 'great' perhaps stressing the size and prowess of the species,[23] and "white shark" having historically been used to describe the much smaller oceanic white-tipped shark, later referred to for a time as the "lesser white shark". Most scientists prefer 'white shark', as the name "lesser white shark" is no longer used,[23] while some use 'white shark' to refer to all members of the Lamnidae.[20]
The scientific genus name Carcharodon literally means "jagged tooth", a reference to the large serrations that appear in the shark's teeth. It is a portmanteau of two Ancient Greek words: the prefix carchar- is derived from κάρχαρος (kárkharos), which means "jagged" or "sharp". The suffix -odon is a romanization of ὀδών (odṓn), a which translates to "tooth". The specific name carcharias is a Latinization of καρχαρίας (karkharías), the Ancient Greek word for shark.[19] The great white shark was one of the species originally described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae, in which it was identified as an amphibian and assigned the scientific name Squalus carcharias, Squalus being the genus that he placed all sharks in.[24] By the 1810s, it was recognized that the shark should be placed in a new genus, but it was not until 1838 when Sir Andrew Smith coined the name Carcharodon as the new genus.[25]
There have been a few attempts to describe and classify the great white before Linnaeus. One of its earliest mentions in literature as a distinct type of animal appears in Pierre Belon's 1553 book De aquatilibus duo, cum eiconibus ad vivam ipsorum effigiem quoad ejus fieri potuit, ad amplissimum cardinalem Castilioneum. In it, he illustrated and described the shark under the name Canis carcharias based on the jagged nature of its teeth and its alleged similarities with dogs.[a] Another name used for the great white around this time was Lamia, first coined by Guillaume Rondelet in his 1554 book Libri de Piscibus Marinis, who also identified it as the fish that swallowed the prophet Jonah in biblical texts.[26] Linnaeus recognized both names as previous classifications.[24]


