A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9

The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500–1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).
The first early European modern humans appear in the fossil record about 48,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic era. Settled agriculture marked the Neolithic era, which spread slowly across Europe from southeast to the north and west. The later Neolithic period saw the introduction of early metallurgy and the use of copper-based tools and weapons, and the building of megalithic structures, as exemplified by Stonehenge. During the Indo-European migrations, Europe saw migrations from the east and southeast. The period known as classical antiquity began with the emergence of the city-states of ancient Greece. Later, the Roman Empire came to dominate the entire Mediterranean Basin. The Migration Period of the Germanic people began in the late 4th century AD and made gradual incursions into various parts of the Roman Empire.
The fall of the Western Roman Empire in AD 476 traditionally marks the start of the Middle Ages. While the Eastern Roman Empire would continue for another 1000 years, the former lands of the Western Empire would be fragmented into a number of different states. At the same time, the early Slavs began to become established as a distinct group in the central and eastern parts of Europe. The first great empire of the Middle Ages was the Frankish Empire of Charlemagne, while the Islamic conquest of Iberia established Al-Andalus. The Viking Age saw a second great migration of Norse peoples. Attempts to retake the Levant from the Muslim states that occupied it made the High Middle Ages the age of the Crusades, while the political system of feudalism came to its height. The Late Middle Ages were marked by large population declines, as Europe was threatened by the bubonic plague, as well as invasions by the Mongol peoples from the Eurasian Steppe. At the end of the Middle Ages, there was a transitional period, known as the Renaissance.
Early Modern Europe is usually dated to the end of the 15th century. Technological changes such as gunpowder and the printing press changed how warfare was conducted and how knowledge was preserved and disseminated. The Reformation saw the fragmentation of religious thought, leading to religious wars. The Age of Exploration led to colonization, and the exploitation of the people and resources of colonies brought resources and wealth to Europe. After 1800, the Industrial Revolution brought capital accumulation and rapid urbanization to Western Europe, while several countries transitioned away from absolutist rule to parliamentary regimes. The Age of Revolution saw long-established political systems upset and turned over. In the 20th century, World War I led to a remaking of the map of Europe as the large Empires were broken up into nation-states. Lingering political issues would lead to World War II, during which Nazi Germany perpetrated The Holocaust. After World War II, during the Cold War, most of Europe became divided by the Iron Curtain in two military blocs: NATO and the Warsaw Pact. The post-war period saw decolonization as Western European colonial empires were dismantled. The post-war period also featured the gradual development of the European integration process, which led to the creation of the European Union; this extended to Eastern European countries after the fall of the Berlin Wall. The 21st century saw the European debt crisis, the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
Prehistory of Europe
Paleolithic

Homo erectus migrated from Africa to Europe before the emergence of modern humans. Homo erectus georgicus, which lived roughly 1.8 million years ago in Georgia, is the earliest hominid to have been discovered in Europe.[2] The earliest appearance of anatomically modern people in Europe has been dated to 45,000 BC, referred to as the Early European modern humans. Some locally developed transitional cultures (Uluzzian in Italy and Greece, Altmühlian in Germany, Szeletian in Central Europe and Châtelperronian in the southwest) use clearly Upper Palaeolithic technologies at very early dates.

Nevertheless, the definitive advance of these technologies is made by the Aurignacian culture, originating in the Levant (Ahmarian) and Hungary (first full Aurignacian). By 35,000 BC, the Aurignacian culture and its technology had extended through most of Europe. The last Neanderthals seem to have been forced to retreat to the southern half of the Iberian Peninsula. Around 29,000 BC a new technology/culture appeared in the western region of Europe: the Gravettian. This technology/culture has been theorised to have come with migrations of people from the Balkans (see Kozarnika).
Around 16,000 BC, Europe witnessed the appearance of a new culture, known as Magdalenian, possibly rooted in the old Gravettian. This culture soon superseded the Solutrean area and the Gravettian of mainly France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Poland, Portugal and Ukraine. The Hamburg culture prevailed in Northern Europe in the 14th and the 13th millennium BC as the Creswellian (also termed the British Late Magdalenian) did shortly after in the British Isles. Around 12,500 BC, the Würm glaciation ended. Magdalenian culture persisted until c. 10,000 BC, when it quickly evolved into two microlithist cultures: Azilian (Federmesser), in Spain and southern France, and then Sauveterrian, in southern France and Tardenoisian in Central Europe, while in Northern Europe the Lyngby complex succeeded the Hamburg culture with the influence of the Federmesser group as well.
Neolithic and Copper Age

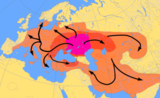
Evidence of permanent settlement dates from the 8th millennium BC in the Balkans. The Neolithic reached Central Europe in the 6th millennium BC and parts of Northern Europe in the 5th and 4th millenniums BC. The modern indigenous populations of Europe are largely descended from three distinct lineages: Mesolithic hunter-gatherers, a derivative of the Cro-Magnon population, Early European Farmers who migrated from Anatolia during the Neolithic Revolution, and Yamnaya pastoralists who expanded into Europe in the context of the Indo-European expansion.[3] The Indo-European migrations started in Southeast Europe at around c. 4200 BC. through the areas around the Black sea and the Balkan peninsula. In the next 3000 years the Indo-European languages expanded through Europe.

Around this time, in the 5th millennium BC the Varna culture evolved. In 4700 – 4200 BC, the Solnitsata town, believed to be the oldest prehistoric town in Europe, flourished.[4][5]
-
Neolithic expansion in Europe, 7000-4000 BC
-
Late Neolithic Europe, c. 5000-3500 BC
Ancient Europe
Bronze Age

The first well-known literate civilization in Europe was the Minoan civilization that arose on the island of Crete and flourished from approximately the 27th century BC to the 15th century BC.[6]
The Minoans were replaced by the Mycenaean civilization which flourished during the period roughly between 1600 BC, when Helladic culture in mainland Greece was transformed under influences from Minoan Crete, and 1100 BC. The major Mycenaean cities were Mycenae and Tiryns in Argolis, Pylos in Messenia, Athens in Attica, Thebes and Orchomenus in Boeotia, and Iolkos in Thessaly. In Crete, the Mycenaeans occupied Knossos. Mycenaean settlement sites also appeared in Epirus,[7][8] Macedonia,[9][10] on islands in the Aegean Sea, on the coast of Asia Minor, the Levant,[11] Cyprus[12] and Italy.[13][14] Mycenaean artefacts have been found well outside the limits of the Mycenean world.

Quite unlike the Minoans, whose society benefited from trade, the Mycenaeans advanced through conquest. Mycenaean civilization was dominated by a warrior aristocracy. Around 1400 BC, the Mycenaeans extended their control to Crete, the centre of the Minoan civilization, and adopted a form of the Minoan script (called Linear A) to write their early form of Greek in Linear B.
The Mycenaean civilization perished with the collapse of Bronze-Age civilization on the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea. The collapse is commonly attributed to the Dorian invasion, although other theories describing natural disasters and climate change have been advanced as well.[citation needed] Whatever the causes, the Mycenaean civilization had definitely disappeared after LH III C, when the sites of Mycenae and Tiryns were again destroyed and lost their importance. This end, during the last years of the 12th century BC, occurred after a slow decline of the Mycenaean civilization, which lasted many years before dying out. The beginning of the 11th century BC opened a new context, that of the protogeometric, the beginning of the geometric period, the Greek Dark Ages of traditional historiography.
The Bronze Age collapse may be seen in the context of a technological history that saw the slow spread of ironworking technology from present-day Bulgaria and Romania in the 13th and the 12th centuries BC.[15]
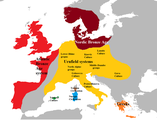
The Tumulus culture and the following Urnfield culture of central Europe were part of the origin of the Roman and Greek cultures.[16]
-
Indo-European migrations from c. 4000-1500 BC according to the Kurgan hypothesis
-
Late Bronze Age Europe, c. 1300-900 BC
Classical Antiquity

Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity,[17] is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and ancient Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia.[18][19]
Ancient Greece
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=History_of_EuropeText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk