A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Prince Edward Island
| |
|---|---|
| Motto(s): | |
| Coordinates: 46°24′N 63°12′W / 46.400°N 63.200°W[2] | |
| Country | Canada |
| Confederation | July 1, 1873 (8th) |
| Capital (and largest city) | Charlottetown |
| Largest metro | Charlottetown |
| Government | |
| • Type | Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| • Lieutenant governor | Antoinette Perry |
| • Premier | Dennis King |
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island |
| Federal representation | Parliament of Canada |
| House seats | 4 of 338 (1.2%) |
| Senate seats | 4 of 105 (3.8%) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 5,660 km2 (2,190 sq mi) |
| • Land | 5,660 km2 (2,190 sq mi) |
| • Water | 0 km2 (0 sq mi) 0% |
| • Rank | 13th |
| 0.1% of Canada | |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 154,331[3] |
| • Estimate (Q1 2024) | 176,162[5] |
| • Rank | 10th |
| • Density | 27.27/km2 (70.6/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Prince Edward Islander, Islander, PEIer |
| Official languages | English (de facto)[6] |
| GDP | |
| • Rank | 10th |
| • Total (2017) | 6.652 billion |
| • Per capita | C$36,740 (13th) |
| HDI | |
| • HDI (2021) | 0.930[7] — Very high (4th) |
| Time zone | UTC-04:00 (Atlantic) |
| Canadian postal abbr. | PE |
| Postal code prefix | |
| ISO 3166 code | CA-PE |
| Flower | Pink lady's slipper |
| Tree | Red oak |
| Bird | Blue jay |
| Rankings include all provinces and territories | |
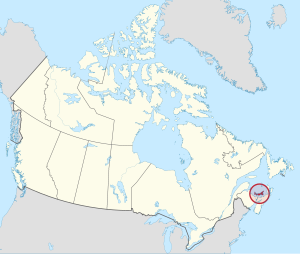
Prince Edward Island (PEI; French: Île-du-Prince-Édouard; Scottish Gaelic: Eilean a' Phrionnsa; colloquially known as The Island) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. While it is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation".[8] Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces.
Part of the traditional lands of the Miꞌkmaq, it was colonized by the French in 1604 as part of the colony of Acadia. The island, known as Isle St-Jean (St-John's Island), was ceded to the British at the conclusion of the Seven Years' War in 1763 and became part of the colony of Nova Scotia. In 1769 the St-John's island became its own British colony and its name was changed to Prince Edward Island (PEI) in 1798. PEI hosted the Charlottetown Conference in 1864 to discuss a union of the Maritime provinces; however, the conference became the first in a series of meetings which led to Canadian Confederation on 1 July 1867. Prince Edward Island initially balked at Confederation but, facing bankruptcy from the Land Question and construction of a railroad, joined as Canada's seventh province on 1 July 1873.
According to Statistics Canada, the province of Prince Edward Island had 176,113 residents in 2023.[9] The backbone of the island economy is farming; it produces 25% of Canada's potatoes. Other important industries include fisheries, tourism, aerospace, biotechnology, information technology and renewable energy.[10] As Prince Edward Island is one of Canada's older settled areas, its population still reflects the origins of its earliest settlers, with Acadian, Scottish, Irish, and English surnames being dominant.
Prince Edward Island is located in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, about 10 km (6 miles) across the Northumberland Strait from both Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. It is about 200 kilometres (120 miles) north of Halifax and 600 kilometres (370 miles) east of Quebec City. It has a land area of 5,686.03 km2 (2,195.39 sq mi),[11] is the 104th-largest island in the world and Canada's 23rd-largest island. It is the only Canadian province consisting solely of an island.
Etymology
The island is known in the Mi'kmaq language of its historic indigenous occupants as Abegweit or Epekwitk, roughly translated as "land cradled in the waves".
When the island was part of Acadia, originally settled by French colonists, its French name was Île Saint-Jean (St. John's Island). In French, the island is today called Île-du-Prince-Édouard (IPE).
The island was split from the British colony of Nova Scotia in 1769, and renamed in 1798 after Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (1767–1820), the fourth son of King George III and, in 1819, father of the future Queen Victoria. Thus, Prince Edward has been called "Father of the Canadian Crown".[12] The following island landmarks are also named after the Duke of Kent:
- Prince Edward Battery, Victoria Park, Charlottetown
- Kent College, established in 1804 by Lieutenant Governor Edmund Fanning and his Legislative Council, the college would eventually become the University of Prince Edward Island
- Kent Street, Charlottetown
- West Kent Elementary School
- Kent Street, Georgetown
In Scottish Gaelic, the island's name is Eilean a' Phrionnsa (lit. "the Island of the Prince", the local form of the longer 'Eilean a' Phrionnsa Iomhair/Eideard'), or Eilean Eòin (literally, "John's Island" in reference to the island's former French name) for some Gaelic speakers in Nova Scotia, though not on PEI.
Geography

Prince Edward Island is located in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, west of Cape Breton Island, north of the Nova Scotia peninsula, and northeast of New Brunswick. Its southern shore bounds the Northumberland Strait. The island has two urban areas, and in total, is the most densely populated province in Canada.
The larger urban area surrounds Charlottetown Harbour, situated centrally on the island's southern shore. It consists of the capital city Charlottetown, the suburban towns of Cornwall and Stratford, and a developing urban fringe. A much smaller urban area developed around Summerside Harbour, situated on the southern shore 40 km (25 mi) west of Charlottetown. This consists primarily of the city of Summerside. As with all natural harbours on the island, Charlottetown and Summerside harbours are created by rias.

The coastline has a combination of long beaches, dunes, red sandstone cliffs, salt water marshes, and numerous bays and harbours. The beaches, dunes and sandstone cliffs consist of sedimentary rock and other material with a high iron concentration, which oxidizes upon exposure to the air. The geological properties of the white silica sand found at Basin Head are unique in the province; the sand grains cause a scrubbing noise as they rub against each other when walked on, and have been called the "singing sands". Large dune fields on the north shore can be found on barrier islands at the entrances to various bays and harbours. The sand dunes at Greenwich are of particular significance as the shifting, parabolic dune system is home to a variety of birds and rare plants, and it is also a site of significant archeological interest.
Climate
The climate of the island is a maritime climate considered to be moderate and strongly influenced by the surrounding Gulf of St-Lawrence.[13][14] As such, it is generally milder than many areas of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia due to the warmer waters of the Gulf of St. Lawrence.[15] The climate is characterized by changeable weather throughout the year; in which specific weather conditions seldom last for long.[14]

During July and August, the average daytime high in PEI is 23 °C (73 °F); however, the temperature can sometimes exceed 30 °C (86 °F) during these months. In the winter months of January and February, the average daytime high is −3.3 °C (26 °F). The Island receives an average yearly rainfall of 855 millimetres (33.7 in) and an average yearly snowfall of 2.85 metres (9.4 ft).
Winters are moderately cold and long but are milder than inland locations, with clashes of cold Arctic air and milder Atlantic air causing frequent temperature swings.[14] The climate is considered to be more humid continental climate than oceanic since the Gulf of St. Lawrence freezes over, thus eliminating any moderation.[14] The mean temperature is −7 °C (19 °F) in January.[15] During the winter months, the island usually has many storms (which may produce rain as well as snow) and blizzards since during this time, storms originating from the North Atlantic or the Gulf of Mexico frequently pass through.[14] Springtime temperatures typically remain cool until the sea ice has melted, usually in late April or early May.
Summers are moderately warm, with the daily maximum temperature only occasionally reaching as high as 30 °C (86 °F). Autumn is a pleasant season, as the moderating Gulf waters delay the onset of frost, although storm activity increases compared to the summer. There is ample precipitation throughout the year, although it is heaviest in the late autumn, early winter and mid spring.
The following climate chart depicts the average conditions of Charlottetown, as an example of the province's climate.
| Climate data for Charlottetown Airport, 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1872–present[a] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.1 (59.2) |
13.3 (55.9) |
24.5 (76.1) |
26.7 (80.1) |
31.7 (89.1) |
32.2 (90.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
36.7 (98.1) |
31.5 (88.7) |
27.8 (82.0) |
21.3 (70.3) |
16.7 (62.1) |
36.7 (98.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −3.4 (25.9) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
0.9 (33.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
14.3 (57.7) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
18.6 (65.5) |
12.3 (54.1) |
6.3 (43.3) |
0.5 (32.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −7.7 (18.1) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
3.1 (37.6) |
9.2 (48.6) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.7 (65.7) |
18.3 (64.9) |
14.1 (57.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
2.9 (37.2) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
5.7 (42.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −12.1 (10.2) |
−11.7 (10.9) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
4.1 (39.4) |
9.6 (49.3) |
14.1 (57.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
1.3 (34.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −32.8 (−27.0) |
−30.6 (−23.1) |
−27.2 (−17.0) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
2.8 (37.0) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−17.2 (1.0) |
−28.1 (−18.6) |
−32.8 (−27.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 101.0 (3.98) |
83.2 (3.28) |
86.3 (3.40) |
83.7 (3.30) |
91.0 (3.58) |
98.8 (3.89) |
79.9 (3.15) |
95.7 (3.77) |
95.9 (3.78) |
112.2 (4.42) |
112.5 (4.43) |
118.1 (4.65) |
1,158.2 (45.60) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 34.1 (1.34) |
29.8 (1.17) |
44.1 (1.74) |
59.7 (2.35) |
87.2 (3.43) |
98.8 (3.89) |
79.9 (3.15) |
95.7 (3.77) |
95.9 (3.78) |
110.3 (4.34) |
93.0 (3.66) |
58.6 (2.31) |
887.1 (34.93) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 73.3 (28.9) |
58.3 (23.0) |
44.1 (17.4) |
24.4 (9.6) |
3.7 (1.5) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.7 (0.7) |
19.2 (7.6) |
65.6 (25.8) |
290.4 (114.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 19.3 | 15.7 | 15.9 | 15.3 | 14.1 | 13.2 | 12.6 | 11.7 | 12.8 | 15.0 | 16.9 | 19.8 | 182.4 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 6.3 | 5.0 | 7.5 | 11.6 | 13.8 | 13.2 | 12.6 | 11.7 | 12.8 | 14.6 | 13.0 | 8.6 | 130.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 17.3 | 13.7 | 12.2 | 6.4 | 0.93 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.03 | 1.0 | 6.4 | 15.3 | 73.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 108.9
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Ile_St._Jean Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Analytika
Antropológia Aplikované vedy Bibliometria Dejiny vedy Encyklopédie Filozofia vedy Forenzné vedy Humanitné vedy Knižničná veda Kryogenika Kryptológia Kulturológia Literárna veda Medzidisciplinárne oblasti Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy Metavedy Metodika Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok. www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk | ||||||||||||