
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9



The Nelder–Mead method (also downhill simplex method, amoeba method, or polytope method) is a numerical method used to find the minimum or maximum of an objective function in a multidimensional space. It is a direct search method (based on function comparison) and is often applied to nonlinear optimization problems for which derivatives may not be known. However, the Nelder–Mead technique is a heuristic search method that can converge to non-stationary points[1] on problems that can be solved by alternative methods.[2]
The Nelder–Mead technique was proposed by John Nelder and Roger Mead in 1965,[3] as a development of the method of Spendley et al.[4]
Overview
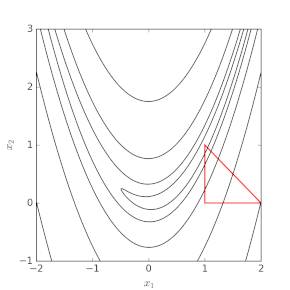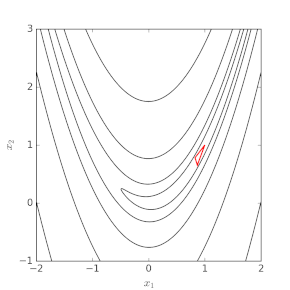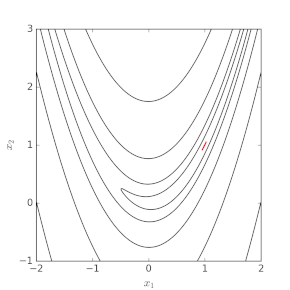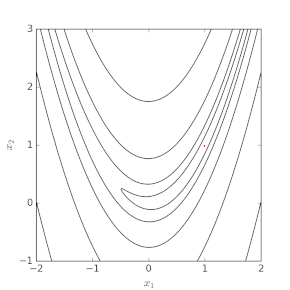
The method uses the concept of a simplex, which is a special polytope of n + 1 vertices in n dimensions. Examples of simplices include a line segment in one-dimensional space, a triangle in two-dimensional space, a tetrahedron in three-dimensional space, and so forth.
The method approximates a local optimum of a problem with n variables when the objective function varies smoothly and is unimodal. Typical implementations minimize functions, and we maximize by minimizing .
For example, a suspension bridge engineer has to choose how thick each strut, cable, and pier must be. These elements are interdependent, but it is not easy to visualize the impact of changing any specific element. Simulation of such complicated structures is often extremely computationally expensive to run, possibly taking upwards of hours per execution. The Nelder–Mead method requires, in the original variant, no more than two evaluations per iteration, except for the shrink operation described later, which is attractive compared to some other direct-search optimization methods. However, the overall number of iterations to proposed optimum may be high.
Nelder–Mead in n dimensions maintains a set of n + 1 test points arranged as a simplex. It then extrapolates the behavior of the objective function measured at each test point in order to find a new test point and to replace one of the old test points with the new one, and so the technique progresses. The simplest approach is to replace the worst point with a point reflected through the centroid of the remaining n points. If this point is better than the best current point, then we can try stretching exponentially out along this line. On the other hand, if this new point isn't much better than the previous value, then we are stepping across a valley, so we shrink the simplex towards a better point. An intuitive explanation of the algorithm from "Numerical Recipes": [5]
The downhill simplex method now takes a series of steps, most steps just moving the point of the simplex where the function is largest (“highest point”) through the opposite face of the simplex to a lower point. These steps are called reflections, and they are constructed to conserve the volume of the simplex (and hence maintain its nondegeneracy). When it can do so, the method expands the simplex in one or another direction to take larger steps. When it reaches a “valley floor”, the method contracts itself in the transverse direction and tries to ooze down the valley. If there is a situation where the simplex is trying to “pass through the eye of a needle”, it contracts itself in all directions, pulling itself in around its lowest (best) point.
Unlike modern optimization methods, the Nelder–Mead heuristic can converge to a non-stationary point, unless the problem satisfies stronger conditions than are necessary for modern methods.[1] Modern improvements over the Nelder–Mead heuristic have been known since 1979.[2]
Many variations exist depending on the actual nature of the problem being solved. A common variant uses a constant-size, small simplex that roughly follows the gradient direction (which gives steepest descent). Visualize a small triangle on an elevation map flip-flopping its way down a valley to a local bottom. This method is also known as the flexible polyhedron method. This, however, tends to perform poorly against the method described in this article because it makes small, unnecessary steps in areas of little interest.
One possible variation of the NM algorithm
(This approximates the procedure in the original Nelder–Mead article.)

We are trying to minimize the function , where . Our current test points are .
1. Order according to the values at the vertices:
- Check whether method should stop. See Termination (sometimes called "convergence").
2. Calculate , the centroid of all points except .
3. Reflection
- Compute reflected point with .
- If the reflected point is better than the second worst, but not better than the best, i.e. ,
- then obtain a new simplex by replacing the worst point with the reflected point , and go to step 1.
4. Expansion
- If the reflected point is the best point so far, ,
- then compute the expanded point with .
- If the expanded point is better than the reflected point, ,
- then obtain a new simplex by replacing the worst point with the expanded point and go to step 1;
- else obtain a new simplex by replacing the worst point with the reflected point and go to step 1.
5. Contraction
- Here it is certain that . (Note that is second or "next" to the worst point.)
- If ,
- then compute the contracted point on the outside with .
- If the contracted point is better than the reflected point, i.e. ,
- then obtain a new simplex by replacing the worst point with the contracted point and go to step 1;
- Else go to step 6;
- If
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk























