
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Pensacola | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top: Pensacola skyline, Pensacola Museum of History, University of West Florida Library, Escambia County Courthouse, William Dudley Chipley Obelisk, National Naval Aviation Museum | |
| Motto: "Florida's First & Future" | |
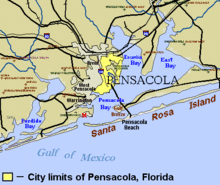
 Location in Escambia County and the state of Florida | |
| Coordinates: 30°25′17″N 87°13′02″W / 30.42139°N 87.21722°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Florida |
| County | Escambia |
| First settled | 1559 |
| Resettled | 1667 |
| Incorporated | 1822[1] |
| Founded by | Don Tristan de Luna |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–Council |
| • Body | Pensacola City Council |
| • Mayor | D. C. Reeves (R) |
| • Council President | Casey Jones |
| • Council Members | Delarian Wiggins, Jennifer Brahier, Allison Patton, Teniadé Broughton, Charles Bare, and Council Vice President Jared Moore |
| • City Administrator | Kerrith Fiddler |
| • City Clerk | Ericka Burnett |
| Area | |
| • City | 41.12 sq mi (106.49 km2) |
| • Land | 22.76 sq mi (58.95 km2) |
| • Water | 18.36 sq mi (47.54 km2) |
| • Metro | 1,669.30 sq mi (4,323.5 km2) |
| Elevation | 102 ft (31 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • City | 54,312 |
| • Density | 2,386.19/sq mi (921.30/km2) |
| • Urban | 390,172 (US: 108th) |
| • Urban density | 1,486.2/sq mi (573.8/km2) |
| • Metro | 509,905 (US: 110th) |
| • Metro density | 1,669.30/sq mi (644.52/km2) |
| Demonym | Pensacolian |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| ZIP codes | 32501-32509, 32511-32514, 32516, 32520-32524, 32526, 32534, 32559, 32573-32576, 32581, 32582, 32589-32598 |
| Area code(s) | 850, 448 |
| FIPS code | 12-55925[3] |
| GNIS feature ID | 0294117[4] |
| Website | www |
Pensacola (/ˌpɛnsəˈkoʊlə/ PEN-sə-KOH-lə) is the westernmost and largest city in the Florida Panhandle. It is the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County.[5] At the 2020 census, the population was 54,312, up from 51,923 at the 2010 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola Metropolitan Statistical Area, which had 509,905 residents in 2020.
Pensacola was first settled by the Spanish in 1559, predating the establishment of St. Augustine by six years, but was abandoned due to a hurricane and not re-established until 1698.[citation needed] Pensacola is a seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located in Pensacola. It is the base of the Blue Angels flight demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The University of West Florida is situated north of the city center.
The area was originally inhabited by Muskogean-speaking peoples.[citation needed] The Pensacola people lived there at the time of European contact, and Creek people frequently visited and traded from present-day southern Alabama and Mississippi and southeast of Louisiana. Spanish explorer Tristán de Luna founded a short-lived settlement in 1559.[6] In 1698 the Spanish established a presidio in the area, from which the modern city gradually developed. The area changed hands several times as European powers competed in North America. During Florida's British rule (1763–1781), fortifications were strengthened.[citation needed]
It is nicknamed "The City of Five Flags", due to the five governments that have ruled it during its history: the flags of Spain (Castile), France, Great Britain, the United States of America, and the Confederate States of America. Other nicknames include "World's Whitest Beaches" (due to the white sand of Florida panhandle beaches), "Cradle of Naval Aviation", "Western Gate to the Sunshine State", "America's First Settlement", "Emerald Coast", "Redneck Riviera", and "P-Cola".
History
Spanish Empire 1559–1719, 1722–1763 and 1781–1821
French Empire 1719–1722
British Empire 1763–1781
United States 1821–1861
Confederate States of America 1861–1865
United States 1865 to present
Pre-European
The original inhabitants of the Pensacola Bay area were Native American peoples. At the time of European contact, a Muskogean-speaking tribe known to the Spanish as the Pensacola, lived in the region. This name was not recorded until 1677, but the tribe appears to be the source of the name "Pensacola" for the bay and thence the city.[7] Creek people, also Muskogean-speaking, came regularly from present-day southern Alabama to trade, so the peoples were part of a broader regional and even continental network of relations.[8]
The best-known Pensacola culture site in terms of archeology is the Bottle Creek site, a large site located 59 mi (95 km) west of Pensacola north of Mobile, Alabama. This site has at least 18 large earthwork mounds, five of which are arranged around a central plaza. Its main occupation was from 1250 CE to 1550. It was a ceremonial center for the Pensacola people and a gateway to their society. This site would have had easy access by a dugout canoe, the main mode of transportation used by the Pensacola.[9]
Spanish
The area's written recorded history begins in the 16th century, with documentation by Spanish explorers who were the first Europeans to reach the area. The expeditions of Pánfilo de Narváez in 1528 and Hernando de Soto in 1539 both visited Pensacola Bay, the latter of which documented the name "Bay of Ochuse".[10]
In the age of sailing ships Pensacola was the busiest port on the Gulf of Mexico, having the deepest harbor on the Gulf.[11]

In 1559, Tristán de Luna y Arellano landed with some 1,500 people on 11 ships from Veracruz, Mexico.[12][10][13][14] The expedition was to establish an outpost, ultimately called Santa María de Ochuse by Luna, as a base for Spanish efforts to colonize Santa Elena (present-day Parris Island, South Carolina.) But the colony was decimated by a hurricane on September 19, 1559,[12][10][14] which killed an unknown number of sailors and colonists, sank six ships, grounded a seventh, and ruined supplies.
The survivors struggled to survive, most moving inland to what is now central Alabama for several months in 1560 before returning to the coast; but in 1561, the effort was abandoned.[12][14] Some of the survivors eventually sailed to Santa Elena, but another storm struck there. Survivors made their way to Cuba and finally returned to Pensacola, where the remaining fifty at Pensacola were taken back to Veracruz. The Viceroy's advisers later concluded that northwest Florida was too dangerous to settle. They ignored it for 137 years.[12][14]
In the late 17th century, the French began exploring the lower Mississippi River with the intention of colonizing the region as part of La Louisiane or New France in North America. Fearful that Spanish territory would be threatened, the Spanish founded a new settlement in western Florida. In 1698 they established a fortified town near what is now Fort Barrancas, laying the foundation for permanent European-dominated settlement of the modern city of Pensacola.[15] The Spanish built three presidios in Pensacola:[16]
- Presidio Santa Maria de Galve (1698–1719): the presidio included fort San Carlos de Austria (east of present Fort Barrancas) and a village with church;[16]
- Presidio Isla de Santa Rosa (1722–1752): this next presidio was on western Santa Rosa Island near the site of present Fort Pickens, but hurricanes battered the island in 1741 and 1752. The garrison was moved to the mainland;[16]
- Presidio San Miguel de Panzacola (1754–1763): the final presidio was built about 5 mi (8 km) east of the first presidio; the present-day historic district of downtown Pensacola, named from "Panzacola", developed around the fort.[16]
During the early years of settlement, a triracial creole society developed. As a fortified trading post, the Spanish had mostly men stationed here. Some married or had unions with Pensacola, Creek or African women, both slave and free, and their descendants created a mixed-race population of mestizos and mulattos. The Spanish encouraged fugitive slaves from the Southern colonies to come to Florida as a refuge, promising freedom in exchange for conversion to Catholicism. Most went to the area around St. Augustine,[17] but escaped slaves also reached Pensacola.
British

After years of settlement, the Spanish ceded Florida to the British in 1763 as a result of an exchange following British victory over both France and Spain in the French and Indian War (the North American theater of the Seven Years' War), and French cession of its territories in North America. The British designated Pensacola as the capital of their new colony of West Florida. From 1763, the British strengthened defenses around the mainland area of fort San Carlos de Barrancas, building the Royal Navy Redoubt. George Johnstone was appointed as the first British Governor, and in 1764 a colonial assembly was established.[18][19] The structure of the colony was modeled after the existing British colonies in America, as opposed to French Canada, which was based on a different structure. West Florida was invited to send delegates to the First Continental Congress which was convened to present colonial grievances against the British Parliament to George III, but along with several other colonies, including East Florida, they declined the invitation. Once the American War of Independence had broken out, the colonists remained overwhelmingly loyal to the Crown. In 1778 the Willing Expedition proceeded with a small force down the Mississippi, ransacking estates and plantations, until they were eventually defeated by a local militia. In the wake of this, the area received a small number of British reinforcements.
British military resources were limited and Pensacola ranked fairly low on their list of priorities. For this reason only small token amounts of British military forces were ever sent to defend Pensacola. This was in contrast to colonies such as South Carolina, where large numbers of British soldiers were sent.[20] After Spain joined the American Revolution in 1779 on the side of the rebels, Spanish forces captured the city in the 1781 Siege of Pensacola, gaining control of West Florida.[13] After the war, the British officially ceded both West Florida and East Florida to Spain as part of the post-war peace settlement.
In 1785 many Creek from southern Alabama and Georgia came to trade and Pensacola developed as a major trade center. It was a garrison town, predominantly males in the military or trade.[8] Americans made raids into the area, and settlers pressured the federal government to gain control of this territory.
United States
In the final stages of the War of 1812, American troops launched an offensive on Pensacola against the Spanish and British garrisons protecting the city, which surrendered after two days of fighting. Pensacola was conquered again by the US in 1818. In 1819, Spain and the United States negotiated the Adams–Onís Treaty, by which Spain recognized the American control over Florida in exchange of the American recognition of Spanish control over Texas.[13] A Spanish census of 1820 indicated 181 households in the town, with a third of mixed-blood. The people were predominantly French and Spanish Creole. Indians in the area were noted through records, travelers' accounts, and paintings of the era, including some by George Washington Sully and George Catlin. Creek women were also recorded in marriages to Spanish men, in court records or deeds.[8]
In 1821, with Andrew Jackson as provisional governor, Pensacola became part of the United States.[13] The city was officially incorporated as a municipality in 1822.[1] The Creek continued to interact with European Americans and African Americans, but the dominant whites increasingly imposed their binary racial classifications: white and black ("colored", within which were included free people of color, including Indians). However, American Indians and mestizos were identified separately in court and Catholic church records, and as Indians in censuses up until 1840, attesting to their presence in the society. After that, the Creek were not separately identified as Indian, but the people did not disappear. Even after removal of many Seminole to Indian Territory, Indians, often of mixed-race but culturally identifying as Muskogean, lived throughout Florida.[8]
St. Michael's Cemetery was established in the 18th century at a location in a south central part of the city, which developed as the Downtown area. Initially owned by the Church of St. Michael, it is now owned and managed by St. Michael's Cemetery Foundation of Pensacola, Inc.[21] Preliminary studies indicate that there are over 3,200 marked burials as well as a large number unmarked.[21]
Tensions between the white community and Indians tended to increase during the Removal era. In addition, an increasing proportion of Anglo-Americans, who constituted the majority of whites by 1840, led to a hardening of racial discrimination in the area.[8] There was disapproval of white men living with women of color, which had previously been accepted. In 1853 the legislature passed a bill prohibiting Indians from living in the state, and provided for capture and removal to Indian Territory.[8]

While the bill excluded mixed-Indians and those already living in white communities, they went "underground" to escape persecution. No Indians were listed in late 19th and early 20th century censuses for Escambia County. People of Indian descent were forced into the white or black communities by appearance, and officially, in terms of records, "disappeared". It was a pattern repeated in many Southern settlements. Children of white fathers and Indian mothers were not designated as Indian in the late 19th century, whereas children of blacks or mulattos were classified within the black community, related to laws during the slavery years.[8]
Pensacola experienced the Civil War when in 1861 Confederate forces lost the nearby Battle of Santa Rosa Island and federal forces of the United States subsequently failed to win the Battle of Pensacola. After the fall of New Orleans in 1862 the Confederacy abandoned the city and it was occupied by the North.[22] In June, 1861, the Pensacola Guards were mustered in as a company in the 1st Florida Infantry Regiment.[23]
In 1907–1908 there were 116 Creek in Pensacola who applied for the Eastern Cherokee enrollment, thinking that all Indians were eligible to enroll. Based on Alabama census records, most of these individuals have been found to be descendants of Creek who had migrated to the Pensacola area from southern Alabama after Indian removal of the 1830s.[8]
In 1908, a citywide streetcar strike occurred in the city, this led to state militia being stationed in the city and marital law being declared.[24][25]
Geography
Pensacola is located on the north side of Pensacola Bay. It is 59 mi (95 km) east of Mobile, Alabama, and 196 mi (315 km) west of Tallahassee, the capital of Florida. Although the incorporated city limits of Pensacola are relatively small, there are numerous census designated places (CDPs) located immediately outside of the incorporated city limits that are widely considered to be Pensacola. Due to their proximity to the city limits, their mailing addresses being listed as Pensacola, and lack of independent government services apart from the City of Pensacola and Escambia County. While residents of these CDPs have rejected incorporation into the City of Pensacola in previous referendums, they largely identify as residents of Pensacola. Examples of these CDPs include Goulding, Ferry Pass, Ensley, Bellview, Myrtle Grove, Warrington, and West Pensacola.
According to the United States Census Bureau, Pensacola has a total area of 40.7 sq mi (105.4 km2), consisting of 22.5 sq mi (58.4 km2) of land and 18.1 sq mi (47.0 km2), 44.62%, water.[26]
The land is sloped up northward from Pensacola Bay, with most of the city at an elevation above that which a potential hurricane storm surge could affect.[27]
Climate
Weather statistics since the late 20th century have been recorded at the airport. The city has seen single digit temperatures (below −12 °C) on three occasions: 5 °F (−15 °C) on January 21, 1985; 7 °F (−14 °C) on February 13, 1899; and 8 °F (−13 °C) on January 11, 1982.[28] According to the Köppen climate classification system, Pensacola has a humid subtropical climate,[29] (Köppen Cfa), with short, mild winters and hot, humid summers. Typical summer conditions have highs in the lower 90s °F (32–34 °C) and lows in the mid 70s °F (23–24 °C).[30] Afternoon or evening thunderstorms are common during the summer months. Due partly to the coastal location, temperatures above 100 °F (38 °C) are relatively rare, and last occurred in June 2011, when two of the first four days of the month recorded highs reaching the century mark.[31] The highest temperature ever recorded in the city was 106 °F (41 °C) on July 14, 1980.[30]
In the 1991–2020 climate normals, the daily average temperature in January is 53.2 °F (11.8 °C). Freezing temperatures occur an average of 11 days per winter, with the average first and last dates for a freeze being December 12 and February 14, giving Pensacola an average growing season of 301 days. However, the relatively recent winter season of 2018-19 did not record a freeze, the median first and last freeze dates are earlier and later than the averages of December 12 and February 14, and the median number of freezes per season is 11 or fewer.[32] The mean coldest temperature reached in a given winter season is about 24 °F (−4.4 °C); although the median is slightly higher, at no colder than 25 °F (−3.9 °C) most years, placing Pensacola in USDA zone 9b. Temperatures below 20 °F (−6.7 °C) are very rare, and last occurred on January 8, 2015,[33] when a low of 19 °F (−7.2 °C) was seen.[34] The lowest temperature ever recorded in the city was 5 °F (−15 °C) on January 21, 1985.[30]
Snow is rare in Pensacola, but does occasionally fall. The most recent snowfall event occurred December 9, 2017,[35] and the snow event previous to it occurred on February 12, 2010.[36] The city receives 68.31 in (1,740 mm) of precipitation per year, with a slightly more rainy season in the summer. The rainiest month is July, with 7.89 in (200 mm), with May being the driest month at 3.90 in (99 mm).[30] In June 2012 over one foot (300 mm) of rain fell on Pensacola and adjacent areas, leading to widespread flooding.[37] On April 29, 2014, Pensacola was drenched by at least 20 inches of rain within a 24-hour period, causing the worst flooding in 30 years.[38]
The city suffered a major blow on February 23, 2016, when a large EF3 wedge tornado hit the northwest part of Pensacola, causing major damage and several injuries.[39]
| Climate data for Pensacola, Florida (Pensacola Int'l), 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1879–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 81 (27) |
84 (29) |
90 (32) |
96 (36) |
102 (39) |
102 (39) |
106 (41) |
105 (41) |
102 (39) |
97 (36) |
89 (32) |
81 (27) |
106 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 74.9 (23.8) |
77.4 (25.2) |
82.5 (28.1) |
85.2 (29.6) |
92.6 (33.7) |
95.7 (35.4) |
97.0 (36.1) |
96.2 (35.7) |
94.8 (34.9) |
88.9 (31.6) |
82.3 (27.9) |
77.6 (25.3) |
98.4 (36.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 62.7 (17.1) |
66.4 (19.1) |
72.0 (22.2) |
77.6 (25.3) |
85.1 (29.5) |
90.0 (32.2) |
91.6 (33.1) |
91.0 (32.8) |
88.5 (31.4) |
81.1 (27.3) |
71.8 (22.1) |
65.1 (18.4) |
78.6 (25.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 53.2 (11.8) |
56.8 (13.8) |
62.3 (16.8) |
68.3 (20.2) |
76.0 (24.4) |
81.7 (27.6) |
83.5 (28.6) |
83.0 (28.3) |
80.0 (26.7) |
71.3 (21.8) |
61.4 (16.3) |
55.5 (13.1) |
69.4 (20.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 43.7 (6.5) |
47.2 (8.4) |
52.7 (11.5) |
59.0 (15.0) |
66.9 (19.4) |
73.5 (23.1) |
75.3 (24.1) |
75.0 (23.9) |
71.5 (21.9) |
61.6 (16.4) |
51.0 (10.6) |
45.9 (7.7) |
60.3 (15.7) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 25.7 (−3.5) |
30.2 (−1.0) |
35.1 (1.7) |
44.0 (6.7) |
54.1 (12.3) |
66.7 (19.3) |
70.4 (21.3) |
69.2 (20.7) |
60.3 (15.7) |
44.6 (7.0) |
34.1 (1.2) |
30.5 (−0.8) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 5 (−15) |
7 (−14) |
22 (−6) |
33 (1) |
44 (7) |
55 (13) |
61 (16) |
60 (16) |
43 (6) |
32 (0) Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Pelican_Drop Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Analytika
Antropológia Aplikované vedy Bibliometria Dejiny vedy Encyklopédie Filozofia vedy Forenzné vedy Humanitné vedy Knižničná veda Kryogenika Kryptológia Kulturológia Literárna veda Medzidisciplinárne oblasti Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy Metavedy Metodika Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok. www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk | |||






