
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
| West Germanic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Originally between the Rhine, Alps, Elbe, and North Sea; today worldwide |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-5 | gmw |
| Linguasphere | 52-AB & 52-AC |
| Glottolog | west2793 |
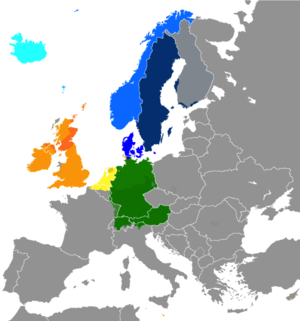 Extent of Germanic languages in present day Europe North Germanic languages West Germanic languages Dots indicate areas where multilingualism is common. | |
 Extent of Germanic languages in present day Africa
West Germanic languages | |
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English and the Frisian languages; Istvaeonic, which encompasses Dutch and its close relatives; and Irminonic, which includes German and its close relatives and variants.
English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German, and Dutch. Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yiddish, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, and Scots. Additionally, several creoles, patois, and pidgins are based on Dutch, English, or German.
History
Origins and characteristics
The Germanic languages are traditionally divided into three groups: West, East and North Germanic.[1] In some cases, their exact relation was difficult to determine from the sparse evidence of runic inscriptions, so that some individual varieties have been difficult to classify. This is especially true for the unattested Jutish language; today, most scholars classify Jutish as a West Germanic variety with several features of North Germanic.[2]
Until the late 20th century, some scholars claimed that all Germanic languages remained mutually intelligible throughout the Migration Period, while others hold that speakers of West Germanic dialects like Old Frankish and speakers of Gothic were already unable to communicate fluently by around the 3rd century AD. As a result of the substantial progress in the study of Proto-West Germanic in the early 21st century, there is a growing consensus that East and West Germanic indeed would have been mutually unintelligible at that time,[3] whereas West and North Germanic remained partially intelligible.[4]
Dialects with the features assigned to the western group formed from Proto-Germanic in the late Jastorf culture (c. 1st century BC). The West Germanic group is characterized by a number of phonological, morphological and lexical innovations or archaisms not found in North and East Germanic. Examples of West Germanic phonological particularities are:[5]
- The delabialization of all labiovelar consonants except word-initially.[6]
- Change of *-zw- and *- đw- to *-ww- e.g. *izwiz > *iwwiz 'you' dat.pl.; *feđwōr > *fewwōr 'four'.[7]
- , the fricative allophone of /d/, becomes in all positions.[8] (The two other fricatives and are retained.). This must have occurred after *-zw- and *- đw- have become *-ww-.[9]
- Replacement of the second-person singular preterite ending -t with -ī (indicative and Subjunctive mood).[10] For more than 150 years there has been a scientific debate on the best explanation of these difficult forms. Today, most linguists, beginning with J. v. Fierlinger in 1885[11] and followed by R. Löwe (1907),[12] O. Behaghel (1922),[13] Jakob Sverdrup (1927), Hermann Hirt (1932),[14] E. Polomé (1964),[15] W. Meid (1971),[16] E. Hill (2004),[17] K.-H. Mottausch[18] and W. Euler (1992ff.)[19] explain(ed) this ending as a relict of the Indo-European aorist tense. Under this assumption, the ending -t would have replaced older -ī(z). Sceptical about this explanation – and mostly explaining these forms as influenced by optative forms – were/are W. Scherer (1868), W. L. van Helten (before 1917), Edward Schröder (1921), Bammesberger (1986) and Don Ringe (2014).
- Loss of word-final /z/.[20][21][22] Only Old High German preserves it at all (as /r/) and only in single-syllable words. Following the later loss of word-final /a/ and /aN/, this made the nominative and accusative of many nouns identical.
- Loss of final *-a (including from PGmc. *-an#) in polysyllables: e.g. acc. sg. OHG horn vs. ORu. horna 'horn'; this change must have occurred after the loss of word-final /z/.[9]
- West Germanic gemination: lengthening of all consonants except /r/ before /j/.;[23][24] this change must have occurred after the loss of final *-a.[9]
- Change of Proto-Germanic *e to i before i and j.[25]
A relative chronology of about 20 sound changes from Proto-Northwest Germanic to Proto-West Germanic (some of them only regional) has been published by Don Ringe in 2014.[26]
A phonological archaism of West Germanic is the preservation of grammatischer Wechsel in most verbs, particularly in Old High German.[27] This implies the same for West Germanic,[28] whereas in East and North Germanic many of these alternations (in Gothic almost all of them) had been levelled out analogically by the time of the earliest texts.
A common morphological innovation of the West Germanic languages is the development of a gerund.[29]
Common morphological archaisms of West Germanic include:
- The preservation of an instrumental case,[30]
- the preservation of the athematic verbs[31] (e.g. Anglo-Saxon dō(m), Old Saxon dōm, OHG. tōm "I do"[32]),
- the preservation of some traces[which?] of the aorist (in Old English and Old High German, but neither in Gothic nor in North Germanic).[33][34]
Furthermore, the West Germanic languages share many lexemes not existing in North Germanic and/or East Germanic – archaisms[35] as well as common neologisms.[36][37] Some lexemes have specific meanings in West Germanic[38] and there are specific innovations in word formation and derivational morphology,[39] for example neologisms ending with modern English -ship (< wgerm. -*skapi, cf. German -schaft) like friendship (< wg. *friund(a)skapi, cf. German Freundschaft) are specific to the West Germanic languages and are thus seen as a Proto West Germanic innovation.[40][41]
Validity of West Germanic as a subgroup
Since at least the early 20th century, a number of morphological, phonological, and lexical archaisms and innovations have been identified as specifically West Germanic. Since then, individual Proto-West Germanic lexemes have also been reconstructed. Yet, there was a long dispute if these West Germanic characteristics had to be explained with the existence of a West Germanic proto-language or rather with Sprachbund effects. Hans Frede Nielsen's 1981 study Old English and the Continental Germanic Languages[42] made the conviction grow that a West Germanic proto-language did exist. But up until the 1990s, some scholars doubted that there was once a Proto-West Germanic proto-language which was ancestral only to later West Germanic languages.[43] In 2002, Gert Klingenschmitt presented a series of pioneering reconstructions of Proto-West Germanic morphological paradigmas and new views on some early West Germanic phonological changes,[44] and in 2013 the first monographic analysis and description of Proto-West Germanic was published (second edition 2022).[45]
Today, there is a scientific consensus[46] on what Don Ringe stated in 2012, that "these changes amount to a massive evidence for a valid West Germanic clade".[47]
After East Germanic broke off (an event usually dated to the 2nd or 1st century BC), the remaining Germanic languages, the Northwest Germanic languages, divided into four main dialects:[48][obsolete source] North Germanic, and the three groups conventionally called "West Germanic", namely:
- Northwest Germanic
- North Sea Germanic, ancestral to Anglo-Frisian and Old Saxon
- Weser–Rhine Germanic, ancestral to Old Dutch and present as a substrate or superstrate in some of the Central Franconian and Rhine Franconian dialects of Old High German
- Elbe Germanic, ancestral to the Upper German and most Central German dialects of Old High German, and the extinct Langobardic language.
Although there is quite a bit of knowledge about North Sea Germanic or Anglo-Frisian (because of the characteristic features of its daughter languages, Anglo-Saxon/Old English and Old Frisian), linguists know almost nothing about "Weser–Rhine Germanic" and "Elbe Germanic". In fact, both terms were coined in the 1940s to refer to groups of archaeological findings, rather than linguistic features. Only later were the terms applied to hypothetical dialectal differences within both regions. Even today, the very small number of Migration Period runic inscriptions from the area, many of them illegible, unclear or consisting only of one word, often a name, is insufficient to identify linguistic features specific to the two supposed dialect groups.
Evidence that East Germanic split off before the split between North and West Germanic comes from a number of linguistic innovations common to North and West Germanic,[5] including:
- The lowering of Proto-Germanic ē (/ɛː/, also written ǣ) to ā.[49]
- The development of umlaut.
- The rhotacism of /z/ to /r/.
- The development of the demonstrative pronoun ancestral to English this.
Under that view, the properties that the West Germanic languages have in common, separate from the North Germanic languages, are not necessarily inherited from a "Proto-West Germanic" language, but may have spread by language contact among the Germanic languages spoken in Central Europe, not reaching those spoken in Scandinavia or reaching them much later. Rhotacism, for example, was largely complete in West Germanic while North Germanic runic inscriptions still clearly distinguished the two phonemes. There is also evidence that the lowering of ē to ā occurred first in West Germanic and spread to North Germanic later since word-final ē was lowered before it was shortened in West Germanic, but in North Germanic the shortening occurred first, resulting in e that later merged with i. However, there are also a number of common archaisms in West Germanic shared by neither Old Norse nor Gothic. Some authors who support the concept of a West Germanic proto-language claim that, not only shared innovations can require the existence of a linguistic clade, but also that there are archaisms that cannot be explained simply as retentions later lost in the North or East, because this assumption can produce contradictions with attested features of the other branches.
The debate on the existence of a Proto-West Germanic clade was summarized (2006):
That North Germanic is ... a unitary subgroup is completely obvious, as all of its dialects shared a long series of innovations, some of them very striking. That the same is true of West Germanic has been denied, but I will argue in vol. ii that all the West Germanic languages share several highly unusual innovations that virtually force us to posit a West Germanic clade. On the other hand, the internal subgrouping of both North Germanic and West Germanic is very messy, and it seems clear that each of those subfamilies diversified into a network of dialects that remained in contact for a considerable period of time (in some cases right up to the present).[50]
The reconstruction of Proto-West Germanic
Several scholars have published reconstructions of Proto-West Germanic morphological paradigms[51] and many authors have reconstructed individual Proto-West Germanic morphological forms or lexemes. The first comprehensive reconstruction of the Proto-West Germanic language was published in 2013 by Wolfram Euler,[52] followed in 2014 by the study of Donald Ringe and Ann Taylor.[53]
Dating Early West Germanic
If indeed Proto-West Germanic existed, it must have been between the 2nd and 7th centuries. Until the late 2nd century AD, the language of runic inscriptions found in Scandinavia and in Northern Germany were so similar that Proto-North Germanic and the Western dialects in the south were still part of one language ("Proto-Northwest Germanic").
Sometime after that, the split into West and North Germanic occurred. By the 4th and 5th centuries the great migration set in. By the end of the 6th century, the area in which West Germanic languages were spoken, at least by the upper classes, had tripled compared to the year 400. This caused an increasing disintegration of the West Germanic language and finally the formation of the daughter languages.[54]
It has been argued that, judging by their nearly identical syntax, the West Germanic dialects were closely enough related to have been mutually intelligible up to the 7th century.[55] Over the course of this period, the dialects diverged successively. The High German consonant shift that occurred mostly during the 7th century AD in what is now southern Germany, Austria, and Switzerland can be considered the end of the linguistic unity among the West Germanic dialects, although its effects on their own should not be overestimated. Bordering dialects very probably continued to be mutually intelligible even beyond the boundaries of the consonant shift.
Middle Ages

During the Early Middle Ages, the West Germanic languages were separated by the insular development of Old and Middle English on one hand, and by the High German consonant shift on the continent on the other.
The High German consonant shift distinguished the High German languages from the other West Germanic languages. By early modern times, the span had extended into considerable differences, ranging from Highest Alemannic in the South (the Walliser dialect being the southernmost surviving German dialect) to Northern Low Saxon in the North. Although both extremes are considered German, they are not mutually intelligible. The southernmost varieties have completed the second sound shift, whereas the northern dialects remained unaffected by the consonant shift.
Of modern German varieties, Low German is the one that most resembles modern English. The district of Angeln (or Anglia), from which the name English derives, is in the extreme northern part of Germany between the Danish border and the Baltic coast. The area of the Saxons (parts of today's Schleswig-Holstein and Lower Saxony) lay south of Anglia. The Angles and Saxons, two Germanic tribes, in combination with a number of other peoples from northern Germany and the Jutland Peninsula, particularly the Jutes, settled in Britain following the end of Roman rule in the island. Once in Britain, these Germanic peoples eventually developed a shared cultural and linguistic identity as Anglo-Saxons; the extent of the linguistic influence of the native Romano-British population on the incomers is debatable.

Family tree
This section needs additional citations for verification. (August 2023) |

Divisions between subfamilies of continental Germanic languages are rarely precisely defined; most form dialect continua, with adjacent dialects being mutually intelligible and more separated ones not.
- West Germanic languages
- North Sea Germanic / Ingvaeonic languages
- Anglo-Frisian
- Anglic
- Frisian
- West Frisian
- Hindeloopen Frisian
- Schiermonnikoog Frisian
- Westlauwers–Terschellings
- Terschelling Frisian
- Mainland West Frisian
- Clay Frisian
- Wood Frisian
- East Frisian
- North Frisian
- West Frisian
- Low German
- Anglo-Frisian
- Weser–Rhine Germanic / Istvaeonic languages
- Low Franconian
- Central German
- Central Franconian
- Rhine Franconian, including the dialects of Hessen, Pennsylvania German, and most of those from Lorraine
- Thuringian
- Upper Saxon German
- Schlesisch–Wilmesau
- Bielsko-Biała[citation needed]
- Silesian (moribund)
- High Prussian (moribund)
- Elbe Germanic / Irminonic languages
- Upper German
- Alemannic, including Swiss German and Alsatian
- Swabian
- Bavarian
- East Franconian
- South Franconian
- Lombardic (extinct)
- Upper German
- Yiddish (a language based on Eastern-Central dialects of late Middle High German/Early New High German)
- North Sea Germanic / Ingvaeonic languages
Comparison of phonological and morphological features
The following table shows a list of various linguistic features and their extent among the West Germanic languages, organized roughly from northwest to southeast. Some may only appear in the older languages but are no longer apparent in the modern languages.
| Old English | Old Frisian | Old Saxon | Old Dutch | Old Central German |
Old Upper German | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palatalisation of velars | Yes | Yes | Partial | No | No | No |
| Unrounding of front rounded vowels | ø but not y | Yes | No | Southwestern | No | No |
| Loss of intervocalic *-h- | Yes | Yes | Developing | Yes | Developing | No |
| Class II weak verb ending *-(ō)ja- | Yes | Yes | Sometimes | No | No | No |
| Merging of plural forms of verbs | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law | Yes | Yes | Yes | Rare | No | No |
| Loss of the reflexive pronoun | Yes | Yes | Most dialects | Most dialects | No | No |
| Loss of final *-z in single-syllable words | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Reduction of weak class III to four relics | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Monophthongization of *ai, *au | Yes | Yes | Yes | Usually | Partial | Partial |
| Diphthongization of *ē, *ō | No | No | Rare | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Final-obstruent devoicing | No | No | No | Yes | Developing | No |
| Loss of initial *h- before consonant | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Developing |
| Loss of initial *w- before consonant | No | No | No | No | Most dialects | Yes |
| High German consonant shift | No | No | No | No | Partial | Yes |
The following table shows some comparisons of consonant development in the respective dialect/language (online examples though) continuum, showing the gradually growing partake in the High German consonant shift and the anglofrisian palatalization. The table uses IPA, to avoid confusion via orthographical differences. The realisation of will be ignored.
C = any consonant, A = back vowel, E = front vowel
| Proto West Germanic | *θ- | *-ð- | *-β- | *-β | *g- | *-Aɣ- | *-Eɣ- | *-Ak- | *-Ak | *-Ek- | *-Ek | *d- | *-d- | *b- | *sA- | *sE- | *sk | *-t- | *-p- | *-tt- | *t- | *-pp- | *p- | *-kk- | *kA- | *kE- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR-English | θ | ð | v | f | ??? (f/ɣ/θ/ð) | k | t̠ʃ | d | b | s | ʃ | ʃ | t | p | t | p | p | k | k | t̠ʃ | ||||||
| Frisian | t | ɾ~d | k | sk | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| South Low Franconian | d | d | ɣ | z | sx | k | ||||||||||||||||||||
| North Low Franconian (Dutch) | x | x | ç | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| West Low German | ʃ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North/Central Low German | g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| East Low German | ʝ | ʃ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| West Central German | x | ç | x | ʃ | t | t͡s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mid Central German | ɾ | b | ɣ | ʝ | ɣ | x | ʒ | ʃ | d | z | v | b | g | |||||||||||||
| East Central German | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Proto-West_Germanic||||||||||||||||||||||||||

