
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
 | |
| Formation | 15 March 2006 |
|---|---|
| Type | Subsidiary organ |
| Legal status | Active |
| Headquarters | Geneva, Switzerland |
President | |
Parent organization | United Nations General Assembly |
| Website | www.ohchr.org |
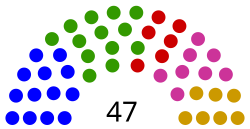
African States (13) Asia-Pacific States (13) Eastern European States (6) Latin American and Caribbean States (8) Western European and Other States (7) | |
"All victims of human rights abuses should be able to look to the Human Rights Council as a forum and a springboard for action." — Ban Ki-moon, UN Secretary-General, 2007[1]

The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC)[a] is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world.[3] The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis.[4] The headquarters of the Council are at the United Nations Office at Geneva in Switzerland.
The Council investigates allegations of breaches of human rights in United Nations member states and addresses thematic human rights issues like freedom of association and assembly,[5] freedom of expression,[6] freedom of belief and religion,[7] women's rights,[8] LGBT rights,[9] and the rights of racial and ethnic minorities.[b]
The Council was established by the United Nations General Assembly on 15 March 2006[c] to replace the United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR, herein CHR).[10] The Council works closely with the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) and engages the United Nations special procedures. The Council has been strongly criticized for including member countries that engage in human rights abuses.[11][12]
Structure
The members of the General Assembly elect the members who occupy 47 seats of the Human Rights Council.[13] The term of each seat is three years, and no member may occupy a seat for more than two consecutive terms.[13] The previous CHR had a membership of 53 elected by the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) through a majority of those present and voting.[14]
Sessions
The UNHRC holds regular sessions three times a year, in March, June, and September.[15] The UNHRC can decide at any time to hold a special session to address human rights violations and emergencies, at the request of one-third of the member states.[16] As of November 2023[update], there have been 36 special sessions.[16]
Members
The Council consists of 47 members, elected yearly by the General Assembly for staggered three-year terms. Members are selected via the basis of equitable geographic rotation using the United Nations regional grouping system. Members are eligible for re-election for one additional term, after which they must relinquish their seat.[17]
The seats are distributed along the following lines:[13]
- 13 for the African Group
- 13 for the Asia-Pacific Group
- 6 for the Eastern European Group
- 8 for the Latin American and Caribbean Group
- 7 for the Western European and Others Group
