
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
|
Probability density function 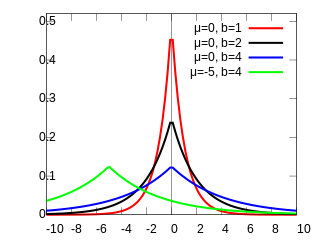 | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function  | |||
| Parameters |
location (real) scale (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Quantile | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| MAD | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Excess kurtosis | |||
| Entropy | |||
| MGF | |||
| CF | |||
| Expected shortfall | [1] | ||
In probability theory and statistics, the Laplace distribution is a continuous probability distribution named after Pierre-Simon Laplace. It is also sometimes called the double exponential distribution, because it can be thought of as two exponential distributions (with an additional location parameter) spliced together along the abscissa, although the term is also sometimes used to refer to the Gumbel distribution. The difference between two independent identically distributed exponential random variables is governed by a Laplace distribution, as is a Brownian motion evaluated at an exponentially distributed random time[citation needed]. Increments of Laplace motion or a variance gamma process evaluated over the time scale also have a Laplace distribution.
Definitions
Probability density function
A random variable has a distribution if its probability density function is
where is a location parameter, and , which is sometimes referred to as the "diversity", is a scale parameter. If and , the positive half-line is exactly an exponential distribution scaled by 1/2.
The probability density function of the Laplace distribution is also reminiscent of the normal distribution; however, whereas the normal distribution is expressed in terms of the squared difference from the mean , the Laplace density is expressed in terms of the absolute difference from the mean. Consequently, the Laplace distribution has fatter tails than the normal distribution. It is a special case of the generalized normal distribution and the hyperbolic distribution. Continuous symmetric distributions that have exponential tails, like the Laplace distribution, but which have probability density functions that are differentiable at the mode include the logistic distribution, hyperbolic secant distribution, and the Champernowne distribution.
Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Laplace_distributionText je dostupný za podmienok Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších podmienok. Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky použitia.
Antropológia
Aplikované vedy
Bibliometria
Dejiny vedy
Encyklopédie
Filozofia vedy
Forenzné vedy
Humanitné vedy
Knižničná veda
Kryogenika
Kryptológia
Kulturológia
Literárna veda
Medzidisciplinárne oblasti
Metódy kvantitatívnej analýzy
Metavedy
Metodika
Text je dostupný za podmienok Creative
Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License 3.0 Unported; prípadne za ďalších
podmienok.
Podrobnejšie informácie nájdete na stránke Podmienky
použitia.
www.astronomia.sk | www.biologia.sk | www.botanika.sk | www.dejiny.sk | www.economy.sk | www.elektrotechnika.sk | www.estetika.sk | www.farmakologia.sk | www.filozofia.sk | Fyzika | www.futurologia.sk | www.genetika.sk | www.chemia.sk | www.lingvistika.sk | www.politologia.sk | www.psychologia.sk | www.sexuologia.sk | www.sociologia.sk | www.veda.sk I www.zoologia.sk


















