
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9



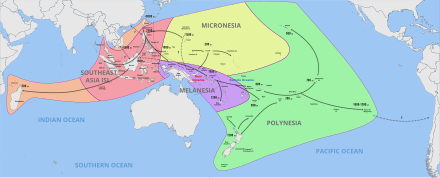
Micronesia (UK: /ˌmaɪkrəˈniːziə/, US: /-ˈniːʒə/)[1] is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples.
The region has a tropical marine climate and is part of the Oceanian realm. It includes four main archipelagos—the Caroline Islands, the Gilbert Islands, the Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands — as well as numerous islands that are not part of any archipelago.
Political control of areas within Micronesia varies depending on the island, and is distributed among six sovereign nations. Some of the Caroline Islands are part of the Republic of Palau and some are part of the Federated States of Micronesia (often shortened to "FSM" or "Micronesia"—not to be confused with the identical name for the overall region). The Gilbert Islands (along with the Phoenix Islands and the Line Islands in Polynesia) comprise the Republic of Kiribati. The Mariana Islands are affiliated with the United States; some of them belong to the U.S. Territory of Guam and the rest belong to the U.S. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. The island of Nauru is its own sovereign nation. The Marshall Islands all belong to the Republic of the Marshall Islands. The sovereignty of Wake Island is contested: it is claimed both by the United States and by the Republic of the Marshall Islands. The United States has actual possession of Wake Island, which is under the immediate administration of the United States Air Force.
Notwithstanding the fact that the notion of "Micronesia" has been quite well established since 1832 and has been used ever since, by most popular works, this set does not correspond to any geomorphological, archaeological, linguistic, ethnic or cultural unity, but on the contrary represents a disparate ensemble, with no real deep unity. In fact, "Micronesian people" does not exist as a subset of the sea-migrating Austronesian people, who may also include the Polynesian people and the hypothetical Australo-Melanesian or "Melanesian people".[2]
Human settlement of Micronesia began several millennia ago.[3] Based on the current scientific consensus, the Austronesian peoples originated from a prehistoric seaborne migration, known as the Austronesian expansion, from pre-Han Formosa, at around 3000 to 1500 BCE. Austronesians reached the northernmost Philippines, specifically the Batanes Islands, by around 2200 BCE. Austronesians were the first people to invent oceangoing sailing technologies (notably catamarans, outrigger boats, lashed-lug boat building, and the crab claw sail), which enabled their rapid dispersal into the islands of the Indo-Pacific.[4][5][6] From 2000 BCE they assimilated (or were assimilated by) the earlier populations on the islands in their migration pathway.[7][8][9][10][11]
The earliest known contact of Europeans with Micronesia was in 1521, when Magellan expedition landed in the Marianas. Jules Dumont d'Urville is usually credited with coining the term "Micronesia" in 1832, but in fact, Louis Domeny de Rienzi used this term a year earlier.[12][13]
Geography
Micronesia is a region in Oceania that includes approximately 2100 islands, with a total land area of 2,700 km2 (1,000 sq mi), the largest of which is Guam, which covers 582 km2 (225 sq mi). The total ocean area within the perimeter of the islands is 7,400,000 km2 (2,900,000 sq mi).[14]
There are four main island groups in Micronesia:
- the Caroline Islands (Federated States of Micronesia and Palau)
- the Gilbert Islands (Kiribati)
- the Mariana Islands (Northern Mariana Islands and Guam, US)
- the Marshall Islands
This does not include the separate island nation of Nauru, along with other distinctly separate islands and smaller island groups.
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands are a widely scattered archipelago consisting of about 500 small coral islands, north of New Guinea and east of the Philippines. The Carolines consist of two nations: the Federated States of Micronesia, consisting of approximately 600 islands on the eastern side of the chain with Kosrae being the most eastern; and Palau consisting of 250 islands on the western side.
Gilbert Islands

The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands, arranged in an approximate north-to-south line. In a geographical sense, the equator serves as the dividing line between the northern Gilbert Islands and the southern Gilbert Islands. The Republic of Kiribati contains all of the Gilberts, including the island of Tarawa, the site of the country's capital.
Mariana Islands

The Mariana Islands are an arc-shaped archipelago made up by the summits of fifteen volcanic mountains. The island chain arises as a result of the western edge of the Pacific Plate moving westward and plunging downward below the Mariana plate, a region that is the most volcanically active convergent plate boundary on Earth. The Marianas were politically divided in 1898, when the United States acquired title to Guam under the Treaty of Paris, 1898, which ended the Spanish–American War. Spain then sold the remaining northerly islands to Germany in 1899. Germany lost all of her colonies at the end of World War I and the Northern Mariana Islands became a League of Nations Mandate, with Japan as the mandatory. After World War II, the islands were transferred into the United Nations Trust Territory System, with the United States as Trustee. In 1976, the Northern Mariana Islands and the United States entered into a covenant of political union under which commonwealth status was granted the Northern Mariana Islands and its residents received United States citizenship.
Marshall Islands

The Marshall Islands are located north of Nauru and Kiribati, east of the Federated States of Micronesia, and south of the U.S. territory of Wake Island. The islands consist of 29 low-lying atolls and 5 isolated islands,[15] comprising 1,156 individual islands and islets. The atolls and islands form two groups: the Ratak Chain and the Ralik Chain (meaning "sunrise" and "sunset" chains). All the islands in the chain are part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands, a presidential republic in free association with the United States. Having few natural resources, the islands' wealth is based on a service economy, as well as some fishing and agriculture. Of the 29 atolls, 24 of them are inhabited.
Bikini Atoll is an atoll in the Marshall Islands. There are 23 islands in the Bikini Atoll. The islands of Bokonijien, Aerokojlol and Nam were vaporized during nuclear tests that occurred there.[16] The islands are composed of low coral limestone and sand.[17] The average elevation is only about 2.1 metres (7 ft) above low tide level.[18]
-
Image of the Castle Bravo nuclear test, detonated on 1 March 1954, at Bikini Atoll
-
An illustration of the Cross Spikes Club[19] of the US Navy on Bikini Atoll, one of several Marshall Islands used for atomic bomb tests.
-
Kili Island is one of the smallest islands in the Marshall Islands.
Nauru
Nauru is an oval-shaped island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, 42 km (26 mi) south of the Equator, listed as the world's smallest republic, covering just 21 km2 (8 sq mi).[20] With 12,511 residents, it is the third least-populated country, after Vatican City and Tuvalu. The island is surrounded by a coral reef, which is exposed at low tide and dotted with pinnacles.[21] The presence of the reef has prevented the establishment of a seaport, although channels in the reef allow small boats access to the island.[22] A fertile coastal strip 150 to 300 m (490 to 980 ft) wide lies inland from the beach.[21]
-
Aerial view of Nauru
-
Nauruan districts of Denigomodu and Nibok
Wake Island
Wake Island is a coral atoll with a coastline of 19 km (12 mi) just north of the Marshall Islands. It is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States. Access to the island is restricted and all activities on the island are managed by the United States Air Force. While geographically adjacent, it is not ethnoculturally part of Micronesia, due to its historical lack of human inhabitation.[citation needed] Micronesians may have possibly visited Wake Island in prehistoric times to harvest fish, but there is nothing to suggest any kind of settlement.[23]
-
Wake Island as depicted by the United States Exploring Expedition, drawn by Alfred Thomas Agate
-
Aerial view Wake Island, looking westward
Geology
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2013) |
The majority of the islands in the area are part of a coral atoll. Coral atolls begin as coral reefs that grow on the slopes of a central volcano. When the volcano sinks back down into the sea, the coral continues to grow, keeping the reef at or above water level. One exception is Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia, which still has the central volcano and coral reefs around it.
Fauna
The Yap Islands host a number of endemic bird species, including the Yap monarch and the Olive white-eye, in addition to four other restricted-range bird species.[24] The endangered Yap flying-fox, though often considered a subspecies of the Pelew flying fox or the Mariana fruit bat, is also endemic to Yap.[24]

This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2013) |
Climate
The region has a tropical marine climate moderated by seasonal northeast trade winds. There is little seasonal temperature variation. The dry season runs from December or January to June and the rainy season from July to November or December. Because of the location of some islands, the rainy season can sometimes include typhoons.
History
Prehistory
The Northern Mariana Islands were the first islands in Oceania colonized by the Austronesian peoples. They were settled by the voyagers who sailed eastwards from the Philippines in approximately 1500 BCE. These populations gradually moved southwards until they reached the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands by 1300 BCE and reconnected with the Lapita culture of the southeast migration branch of Austronesians moving through coastal New Guinea and Island Melanesia. By 1200 BCE, they again began crossing open seas beyond inter-island visibility, reaching Vanuatu, Fiji, and New Caledonia; before continuing eastwards to become the ancestors of the Polynesian people.[25][26][27]
Further migrations by other Austronesians also followed, likely from Sulawesi, settling Palau and Yap by around 1000 BCE. The details of this colonization, however, are not very well known.[25][26][28] In 200 BCE, a loosely connected group of Lapita colonists from Island Melanesia also migrated back northwards, settling the islands of eastern Micronesia almost simultaneously. This region became the center of another wave of migrations radiating outwards, reconnecting them with other settled islands in western Micronesia.[25][26]
Around 800 CE, a second wave of migrants from Southeast Asia arrived in the Marianas, beginning what is now known as the Latte period. These new settlers built large structures with distinctive capped stone pillars known as haligi. They also reintroduced rice (which did not survive earlier voyages), making the Northern Marianas the only islands in Oceania where rice was grown prior to European contact. However, it was considered a high-status crop and only used in rituals. It did not become a staple until after Spanish colonization.[27][29][30]
Construction of Nan Madol, a megalithic complex made from basalt lava logs in Pohnpei, began in around 1180 CE. This was followed by the construction of the Leluh complex in Kosrae in around 1200.[26][31][32]
-
Central Nan Madol (map)
Early European contact

The earliest known contact with Europeans occurred in 1521, when a Spanish expedition under Ferdinand Magellan reached the Marianas.[33] This contact is recorded in Antonio Pigafetta's chronicle of Magellan's voyage, in which he recounts that the Chamorro people had no apparent knowledge of people outside of their island group.[34] A Portuguese account of the same voyage suggests that the Chamorro people who greeted the travellers did so "without any shyness as if they were good acquaintances".[35]
Further contact was made during the sixteenth century, although often initial encounters were very brief. Documents relating to the 1525 voyage of Diogo da Rocha suggest that he made the first European contact with inhabitants of the Caroline Islands, possibly staying on the Ulithi atoll for four months and encountering Yap. Marshall Islanders were encountered by the expedition of Spanish navigator Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón in 1529.[36] Other contact with the Yap islands occurred in 1625.[37]
Colonisation and conversion

In the early 17th century Spain colonized Guam, the Northern Marianas and the Caroline Islands (what would later become the Federated States of Micronesia and the Republic of Palau), creating the Spanish East Indies, which was governed from the Spanish Philippines.
When Russian explorer Otto von Kotzebue visited the Marshall Islands in 1817, he noted that Marshallese families practiced infanticide after the birth of a third child as a form of population planning due to frequent famines.[38]
In 1819, the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions—a Protestant group—brought their Puritan ways to Polynesia. Soon after, the Hawaiian Missionary Society was founded and sent missionaries into Micronesia. Conversion was not met with as much opposition, as the local religions were less developed (at least according to Western ethnographic accounts). In contrast, it took until the end of the 19th to the beginning of the 20th centuries for missionaries to fully convert the inhabitants of Melanesia; however, a comparison of the cultural contrast must take into account the fact that Melanesia has always had deadly strains of malaria present in various degrees and distributions throughout its history (see De Rays Expedition) and up to the present; conversely, Micronesia does not have—and never seems to have had—any malarial mosquitos nor pathogens on any of its islands in the past.[39]
German–Spanish Treaty of 1899
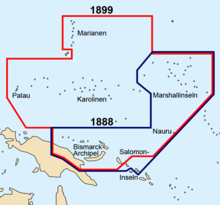
In the Spanish–American War, Spain lost many of its remaining colonies. In the Pacific, the United States took possession of the Spanish Philippines and Guam. On 17 January 1899, the United States also took possession of unclaimed and uninhabited Wake Island. This left Spain with the remainder of the Spanish East Indies, about 6,000 tiny islands that were sparsely populated and not very productive. These islands were ungovernable after the loss of the administrative center of Manila and indefensible after the loss of two Spanish fleets in the war. The Spanish government therefore decided to sell the remaining islands to a new colonial power: the German Empire.
The treaty, which was signed by Spanish Prime Minister Francisco Silvela on 12 February 1899, transferred the Caroline Islands (Kosrae in the east to Palau in the west), the Mariana Islands, and other possessions to Germany. Under German control, the islands became a protectorate and were administered from German New Guinea. Nauru had already been annexed and claimed as a colony by Germany in 1888.
20th century

In the early 20th century, the islands of Micronesia were divided between three foreign powers:
- the United States, which took control of Guam following the Spanish–American War of 1898 and claimed Wake Island;
- Germany, which took Nauru and bought the Marshall, Caroline and Northern Mariana Islands from Spain; and
- the British Empire, which took the Gilbert Islands (Kiribati).
During World War I, Germany's Pacific island territories were seized and became League of Nations mandates in 1923. Nauru became an Australian mandate, while Germany's other territories in Micronesia were given as a mandate to Japan and were named the South Seas Mandate. During World War II, Nauru and Ocean Island were occupied by Japanese troops, with also an occupation of some of the Gilbert Islands and were bypassed by the Allied advance across the Pacific. Following Japan's defeat in World War II its mandate became a United Nations Trusteeship administered by the United States as the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands.[40] Nauru became independent in 1968.
21st century
Today, most of Micronesia are independent states, except for the U.S. Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, Guam and Wake Island, which are U.S. territories.
States and dependencies
| Country | Population (July 2021 estimate)[41][42] | Area (km2) | Population density (/km2) | Urban population | Life expectancy | Literacy rate | Official language(s) | Main religion(s) | Ethnic groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 113,131 | 702 | 158 | 22% | 71.2 | 89% | English | Roman Catholic 50%, Protestant 47%, others 3% | Chuukese 48.8%, Pohnpeian 24.2%, Kosraean 6.2%, Yapese 5.2%, Yap outer islands 4.5%, Asian 1.8%, Polynesian 1.5%, other 7.8% | |
| 170,534 | 540 | 299 | 93% | 78.2 | 99% | English 38.3%, Chamorro 22.2%[43] | Roman Catholic 85%, Buddhism 3.6, other religion 11.4% | Chamorro 37.1%, Filipino 26.3%, other Pacific islander 11.3%, white 6.9%, other 8.6%, mixed 9.8% | |
| 128,874 | 811 | 152 | 44% | 64.0 | 92% | English, Gilbertese (de facto) | Roman Catholic 55%, Protestant 36% | Micronesian 98.8% | |
| 42,050 | 181 | 293 | 71% | 71.5 | 93.7% | Marshallese 98.2%, English | Protestant 54.8%, other Christian 40.6% | Marshallese 92.1%, mixed Marshallese 5.9%, other 2% | |
| 12,511 | 21 | 480 | 100% | 65.0 | 99%[44] | Nauruan[f], English (de facto) | Nauru Congregational Church 35.4%, Roman Catholic 33.2%, Nauru Independent Church (Protestant)[45] 10.4%, Baha'i faith 10%, Buddhism 9% | Nauruan 58%, other Pacific Islander 26%, Chinese 8%, European 8% | |
| 49,481 | 464 | 113 | Zdroj:https://en.wikipedia.org?pojem=Micronesia












