
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | CH | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
 Logo for Core i7 Bloomfield processors | |
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Launched | November 11, 2008 |
| Marketed by | Intel |
| Designed by | Intel |
| Common manufacturer |
|
| Performance | |
| Max. CPU clock rate | 1.06 GHz to 3.33 GHz |
| QPI speeds | 4.80 GT/s to 6.40 GT/s |
| DMI speeds | 2 GT/s |
| Cache | |
| L1 cache | 64 KB per core (32 KB data + 32 KB instructions) |
| L2 cache | 256 KB per core |
| L3 cache | 2 MB to 24 MB shared |
| Architecture and classification | |
| Technology node | 45 nm |
| Microarchitecture | Nehalem |
| Instruction set | x86-16, IA-32, x86-64 |
| Instructions | MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, SSE4.2 |
| Extensions | |
| Physical specifications | |
| Transistors |
|
| Cores |
|
| Sockets | |
| Products, models, variants | |
| Core names |
|
| Product code name |
|
| Models |
|
| History | |
| Predecessors | Core (tock) Penryn (tick) |
| Successors | Westmere (tick) Sandy Bridge (tock) |
| Support status | |
| Unsupported | |
Nehalem /nəˈheɪləm/[1] is the codename for Intel's 45 nm microarchitecture released in November 2008.[2] It was used in the first generation of the Intel Core i5 and i7 processors, and succeeds the older Core microarchitecture used on Core 2 processors.[3] The term "Nehalem" comes from the Nehalem River.[4][5]
Nehalem is built on the 45 nm process, is able to run at higher clock speeds without sacrificing efficiency, and is more energy-efficient than Penryn microprocessors. Hyper-threading is reintroduced, along with a reduction in L2 cache size, as well as an enlarged L3 cache that is shared among all cores. Nehalem is an architecture that differs radically from NetBurst, while retaining some of the latter's minor features.
Nehalem later received a die-shrink to 32 nm with Westmere, and was fully succeeded by "second-generation" Sandy Bridge in January 2011.
Technology
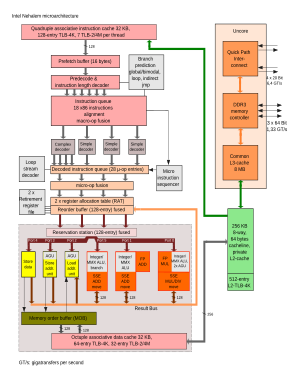
- Cache line block on L2/L3 cache was reduced from 128 bytes in NetBurst & Merom/Penryn to 64 bytes per line in this generation (same size as Yonah and Pentium M).
- Hyper-threading reintroduced.
- Intel Turbo Boost 1.0.[6]
- 2–24 MiB L3 cache with Smart Cache in some models.
- Instruction Fetch Unit (IFU) containing second-level branch predictor with two level Branch Target Buffer (BTB) and Return Stack Buffer (RSB). Nehalem also supports all predictor types previously used in Intel's processors like Indirect Predictor and Loop Detector.[7]
- sTLB (second level unified translation lookaside buffer) (i.e. both instructions and data) that contains 512 entries for small pages only, and is again 4 way associative.[8]
- 3 integer ALU, 2 vector ALU and 2 AGU per core.[9]
- Native (all processor cores on a single die) quad- , hex-, and octa-core processors
- Intel QuickPath Interconnect in HEDT, server, and workstation models and Direct Media Interface on other models replacing the legacy front side bus.
- 64 KB L1 cache per core (32 KB L1 data and 32 KB L1 instruction), and 256 KB L2 cache per core.
- Integration of PCI Express and DMI into the processor in mid-range models, replacing the northbridge.
- Integrated memory controller supporting two or three memory channels of DDR3 SDRAM or four FB-DIMM2 channels.
- Second-generation Intel Virtualization Technology, which introduced Extended Page Table support, virtual processor identifiers (VPIDs), and non-maskable interrupt-window exiting. [10]
- SSE4.2 and
POPCNTinstructions. - Macro-op fusion now works in 64-bit mode.
- 20 to 24 pipeline stages.[11]
Translation lookaside buffer sizes[12] Cache Page Size Name Level 4 KB 2 MB DTLB 1st 64 32 ITLB 1st 128 7 / logical core STLB 2nd 512 none
Performance and power improvements
It has been reported that Nehalem has a focus on performance, thus the increased core size.[13] Compared to Penryn, Nehalem has:
- 10–25% better single-threaded performance / 20–100% better multithreaded performance at the same power level
- 30% lower power consumption for the same performance
- On average, Nehalem provides a 15–20% clock-for-clock increase in performance per core.
Overclocking is possible with Bloomfield processors and the X58 chipset. Lynnfield processors use a PCH removing the need for a northbridge.[14]
Nehalem processors incorporate SSE4.2 SIMD instructions, adding seven new instructions to the SSE 4.1 set in the Core 2 series. The Nehalem architecture reduces atomic operation latency by 50% in an attempt to eliminate overhead on atomic operations such as the LOCK CMPXCHG compare-and-swap instruction.[15]
Variants
| Processing Cores (interface) | Process | Die Size | million transistors | CPUID | Model | Stepping | Mobile | Desktop, UP Server | DP Server | MP Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eight-Core (Quad-Channel) | 45 nm | 684 mm2 | 2.300[16] | 206E6 | 46 | D0 | Beckton (80604) | |||
| Quad-Core (Triple-Channel) | 263 mm2 | 731 | 106A4 106A5 |
26 | C0/C1 D0 |
Bloomfield (80601) | Gainestown (80602) | |||
| Quad-Core (Dual-Channel, PCIe) | 296 mm2 | 774 | 106E4 106E5 |
30 | B0 B1 |
Clarksfield (80607) | Lynnfield (80605) | Jasper Forest (80612) | ||
| Dual-Core (Dual-Channel, PCIe, Graphics Core) | ? | Auburndale (80608) (canceled) | Havendale (80606) (canceled) |
- Lynnfield processors feature 16 PCIe lanes, which can be used in 1x16 or 2x8 configuration.
- 1 6500 series scalable up to 2 sockets, 7500 series scalable up to 4/8 sockets.[17]
Server, workstation, and desktop processors
| Codename | Market | Cores (threads) |
Socket | Processor Branding & Model |
CPU Clock rate |
Turbo | TDP | Interfaces | L3 cache |
Release Date | Price for 1k Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chipset | Memory | ||||||||||||
| Beckton1 | MP Server / DP Server |
8 (16) | LGA 1567 |
Xeon
7000[18] |
X7560 | 2.26 GHz | Yes | 130 W | 4× QPI 6.4 GT/s | DDR3-800 / 1066 (Up to 4x with SMB-Ready motherboard) |
24 MB | 2010-03-30[19] | $3692 |
| X7550 | 2.0 GHz | 18 MB | $2837 | ||||||||||
| X6550 | $2461 | ||||||||||||
| L7555 | 1.86 GHz | 95 W | 4× QPI 5.86 GT/s | 24 MB | $3157 | ||||||||
| 6 (12) | E7540 | 2.0 GHz | 105 W | 4× QPI 6.4 GT/s | 18 MB | $1980 | |||||||
| E6540 | 12 MB | $1712 | |||||||||||
| E7530 | 1.86 GHz | 4× QPI 5.86 GT/s | $1391 | ||||||||||
| L7545 | 95 W | 18 MB | $2087 | ||||||||||
| 6 (6) | X7542 | 2.66 GHz | 130 W | $1980 | |||||||||
| 4 (8) | E7520 | 1.86 GHz | No | 105 W | 4× QPI 4.8 GT/s | $856 | |||||||
| E6510 | 1.73 GHz | 12 MB | $744 | ||||||||||
| Gainestown | DP Server[20] | 4 (8) | LGA 1366 |
Xeon
5000[21] |
W5590 | 3.33 GHz | Yes | 130 W | 2× QPI 6.4 GT/s | 3× DDR3-13331 | 8 MB | 2009-08-09 | $1600 |
| W5580 | 3.2 GHz | 2009-03-29[22] | $1500 | ||||||||||
| X5570 | 2.93 GHz | 95 W | $1286 | ||||||||||
| X5560 | 2.8 GHz | $1072 | |||||||||||
| X5550 | 2.66 GHz | $858 | |||||||||||
| E5540 | 2.53 GHz | 80 W | 2× 5.86 GT/s | 3× DDR3-10661 | $744 | ||||||||
| E5530 | 2.4 GHz | $530 | |||||||||||
| E5520 | 2.26 GHz | $373 | |||||||||||
| L5530 | 2.4 GHz | 60 W | 2009-08-09 | $744 | |||||||||
| L5520 | 2.26 GHz | 2009-03-30 | $530 | ||||||||||
| L5518 | 2.13 GHz | $ | |||||||||||
| 4 (4) | E5507 | 2.26 GHz | No | 80 W | 2× 4.8 GT/s | 3× DDR3-8001 | 4 MB | 2010-03-16 | $266 | ||||
| E5506 | 2.13 GHz | 2009-03-29 | |||||||||||
| L5506 | 2.13 GHz | 60 W | $423 | ||||||||||
| E5504 | 2.0 GHz | 80 W | $224 | ||||||||||
| 2 (4) | L5508 | 2.0 GHz | Yes | 38 W | 2× 5.86 GT/s | 3× DDR3-1066 | 8 MB | $ | |||||
| 2 (2) | E5503 | 2.0 GHz | No | 80 W | 2× 4.8 GT/s | 3× DDR3-800 | 4 MB | 2010-03-16 | $224 | ||||
| E5502 | 1.86 GHz | 2009-03-29 | $188 | ||||||||||
| Jasper
Forest |
4 (8) | EC5549 | 2.53 GHz | Yes | 85 W | 1× 5.86 GT/s | 3× DDR3-1333 | 8 MB | 2010-02-11 | $530 | |||
| LC5528 | 2.13 GHz | 60 W | 1× 4.8 GT/s | 3× DDR3-1066 | $519 | ||||||||
| LC5518 | 1.73 GHz | 48 W | |||||||||||
| 4 (4) | EC5509 | 2 GHz | No | 85 W | $265 | ||||||||
| 2 (4) | EC5539 | 2.27 GHz | 65 W | 1× 5.86 GT/s | 3× DDR3-1333 | 4 MB | $387 | ||||||
| Bloomfield | UP Server[23] | 4 (8) | Xeon
3000[24] |
W3580 | 3.33 GHz | Yes | 130 W | 1× QPI 6.4 GT/s | 3× DDR3-1333 | 8 MB | 2009-08-09 | $999 | |
| W3570 | 3.2 GHz | 2009-03-29[24] | |||||||||||
| W3565 | 3.2 GHz | 1× QPI 4.8 GT/s | 3× DDR3-1066 | 2009-11-01 | $562 | ||||||||
| W3550 | 3.06 GHz | 2009-08-09 | |||||||||||
| W3540 | 2.93 GHz | 2009-03-29[24] | |||||||||||
| W3530 | 2.8 GHz | 2010-03-16 | $294 | ||||||||||
| W3520 | 2.66 GHz | 2009-03-29[24] | $284 | ||||||||||
| 2 (2) | W3505 | 2.53 GHz | No | 4 MB | $ | ||||||||
| W3503 | 2.4 GHz | $ | |||||||||||
| Jasper
Forest |
4 (4) | EC3539 | 2.13 GHz | 65 W | DMI | 8 MB | 2010-02-11 | $302 | |||||
| 2 (4) | LC3528 | 1.73 GHz | Yes | 35 W | 3× DDR3-800 | 4 MB | |||||||
